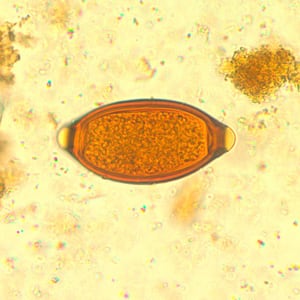
Trichuris trichiura is a helminth (whipworm). Infection is acquired by ingesting eggs from contaminated food, water, or hands. In the USA, cases are seen in southern states.
Adult worms live in the colon. Infection can be light or heavy:
In children, heavy infection can lead to severe anemia, growth retardation, and impaired cognitive development.
Diagnosis is made by identifying eggs in stool samples after concentration methods. The eggs are barrel-shaped with projecting mucus plugs at both ends. Sometimes, adult worms can be seen in the stool.