Enterobius vermicularis is a nematode (roundworm), also called the pinworm. It most commonly affects children, institutionalized persons, and household contacts of infected individuals. Pinworm is the most common helminth infection in the United States.
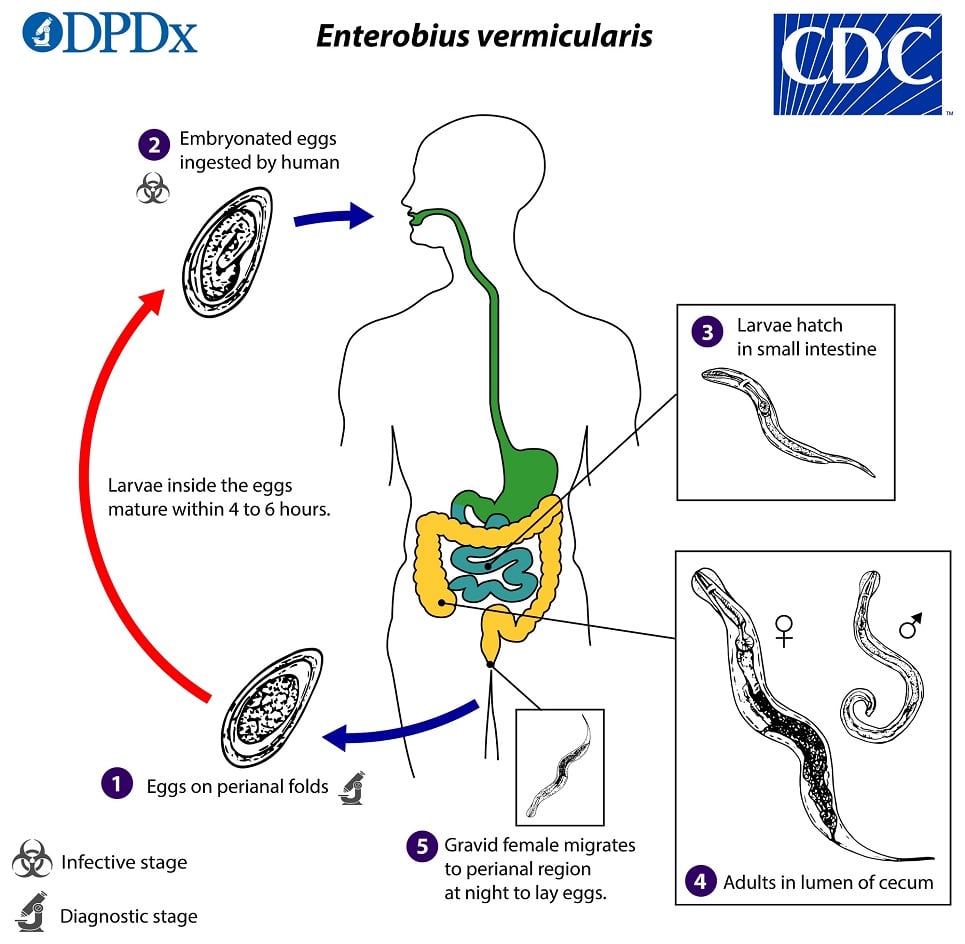
Infection is transmitted directly or indirectly when pinworm eggs are ingested. Common sources include contaminated hands, food, or water.
After ingestion, there is an incubation period of about 1-2 months (or longer) while the adult gravid female matures in the small intestine. Once mature, the adult female migrates to the colon and lays eggs around the anus at night.
Reinfection is common. Rarely, eggs can become airborne, be inhaled, and then swallowed.
Infection is frequently asymptomatic. When symptoms occur, they may include:
Scratching can lead to perianal excoriations and secondary bacterial superinfection.
Diagnosis is made by detecting worms or eggs in the perianal region:
Stool examination and serology are not useful.
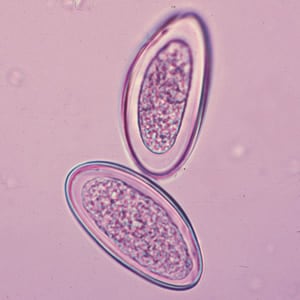
Eggs of E. vermicularis in a wet mount.
Sign up for free to take 1 quiz question on this topic