Acanthamoeba
Acanthamoeba
Acanthamoeba is a free-living amoeba that can infect the eye, skin, and central nervous system (CNS). CNS infection can be rapidly fatal. The trophozoite is the infective form.
Acanthamoeba keratitis can occur after contact lens use and may lead to blindness. The organism typically enters through minor cuts in the skin or is inhaled into the lungs.
Acanthamoeba has been isolated from soil, air, sewage, seawater, chlorinated swimming pools, domestic tap water, bottled water, dental treatment units, hospitals, air-conditioning units, and contact lens cases.
Granulomatous amoebic encephalitis is a severe form that presents acutely with fever, headache, seizures, delirium, and cranial nerve palsies, and it can rapidly progress to death.
Keratitis presents with eye pain, redness, photosensitivity, a foreign body sensation, and eye watering.
Skin lesions present as granulomas.
Diagnosis is made by demonstrating trophozoites in CSF and on brain biopsy. Culture is difficult and is performed as a co-culture with E. coli. For keratitis, corneal scrapings and confocal microscopy can be used for diagnosis.
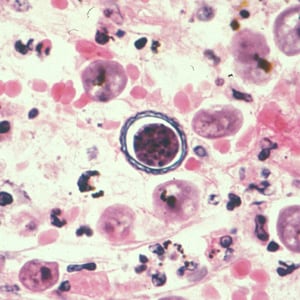
Cyst of Acanthamoeba sp. from brain tissue, stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E).