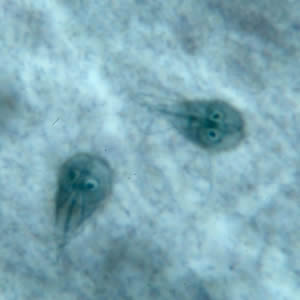
Giardia lamblia
Giardia lamblia
Infection is transmitted by ingesting food or water contaminated with cysts. Cysts are relatively resistant to chlorination, especially in cold water.
It typically presents with diarrhea, gas, greasy stools that tend to float, abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, and dehydration. It may lead to weight loss and malabsorption of fat, lactose, vitamin A, and vitamin B12. Some patients also develop itchy skin, hives, and swelling of the eyes and joints.
For diagnosis, fecal immunoassays are preferred. Stool microscopy shows motile trophozoites with “falling leaf” motility. Cysts can be seen in stool specimens after concentration techniques. A string test (enterotest) can be used to detect trophozoites in bile.
Antigen detection is done by ELISA and direct immunofluorescence. Antibody detection is done by ELISA and indirect immunofluorescence.
G. duodenalis trophozoites in Kohn stain.