Trichomonas exists only in the trophozoite form and shows characteristic wobbling motility. It’s transmitted as an STD and can also spread through contaminated towels and underwear.
Clinically, it presents as vaginitis with:
It’s usually accompanied by:
Diagnosis is made by direct microscopy showing motile trophozoites. Acridine orange or Papanicolaou staining can also be used. Indirect haemagglutination can detect antibodies. ELISA is used for antigen detection. DNA probes and PCR are used for nucleic acid detection.
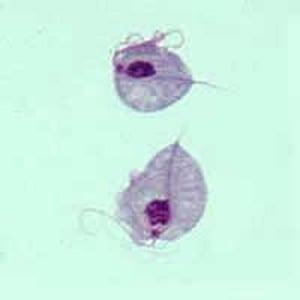
Two trophozoites of T. vaginalis obtained from in vitro culture, stained with Giemsa.