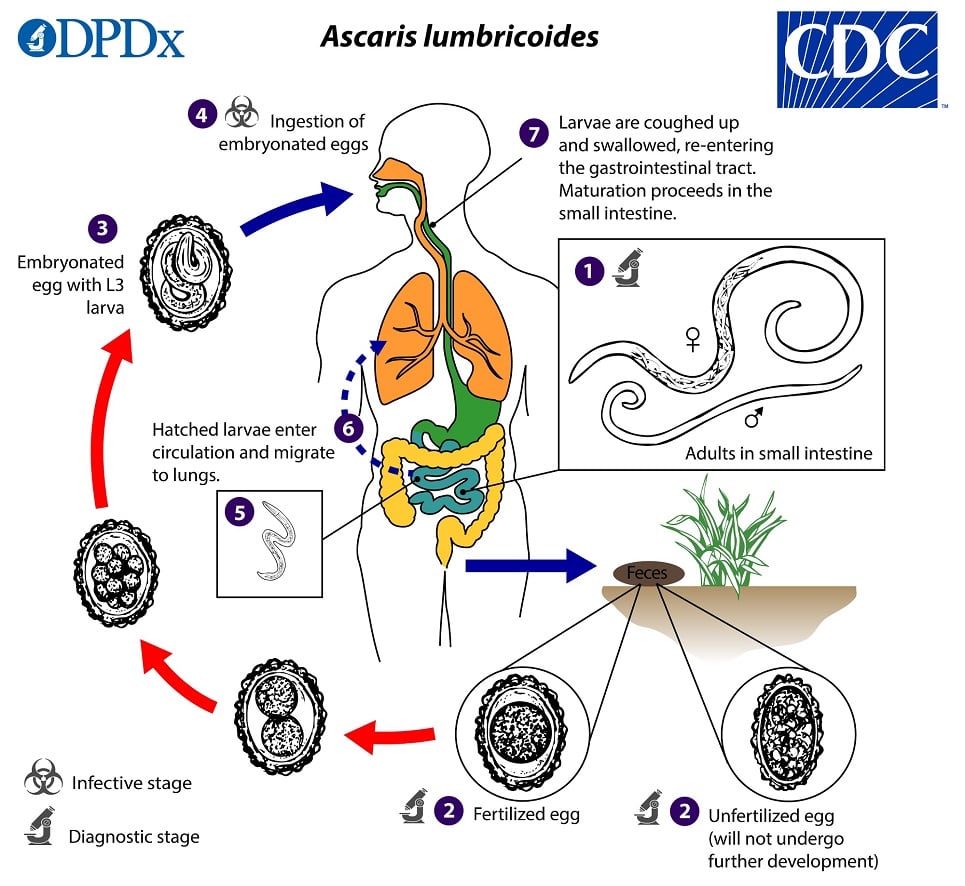
Infection spreads when you ingest fertile eggs from contaminated hands, food, or water. The common pathogens are Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum. A. suum is transmitted from pigs.
After you ingest fertile eggs, they hatch in the small intestine and invade the intestinal mucosa. The larvae then travel through the portal and systemic circulation to the lungs. From the lungs, they either:
Adult worms live in the small intestine.
Infection may be asymptomatic. Heavy infections may present with abdominal pain and discomfort, intestinal obstruction (and sometimes perforation), growth retardation, and malnutrition in children - especially vitamin A deficiency and protein-energy malnutrition.
Migrating adult worms can:
Loeffler’s syndrome is caused by larvae migrating through the lungs. It presents with fever, dry cough, dyspnea, eosinophilia, and urticaria.
Diagnosis is made by demonstrating eggs in stool samples.
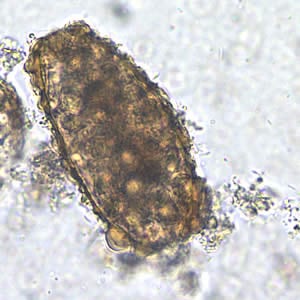
Unfertilized egg of A. lumbricoides in an unstained wet mount, 200x magnification.
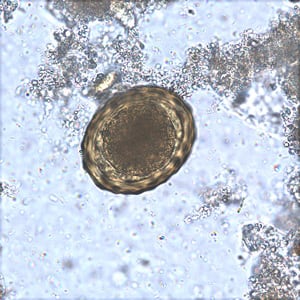
Fertilized egg of A. lumbricoides in an unstained wet mount of stool.