Nervous system
The notochord forms from mesoderm. It induces the overlying ectoderm to become the neural plate. The ectoderm that forms the neural plate is called neuroectoderm.
The neural plate folds and eventually forms the neural tube. The cavity inside the neural tube is the neural canal. The neural canal later gives rise to the ventricles of the brain, the cerebral aqueduct, and the spinal canal.
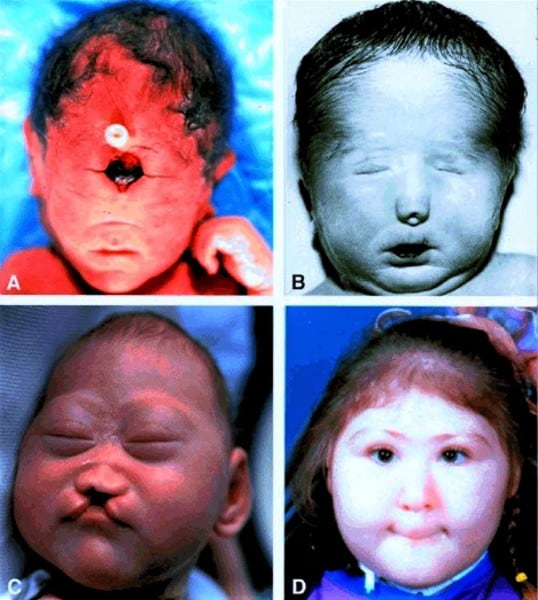
The cranial and caudal openings of the neural tube are called neural pores. They close by days 24-27. Folic acid supplementation prevents open neural tube defects, which occur when this process is disrupted.
The neural tube develops three primary vesicles, which give rise to five secondary vesicles as follows:
| Primary Vesicles | Secondary Vesicles | Derivatives |
|---|---|---|
| Prosencephalon (forebrain) | Telencephalon | Cerebral hemispheres, preoptic area, basal ganglia |
| Diencephalon | Thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus and subthalamus, optic nerve cranial nerve II, retina, neurohypophysis | |
| Mesencephalon (midbrain) | Remains the same | Midbrain |
| Rhombencephalon (hindbrain) | Metencephalon | Pons, cerebellum |
| Myelencephalon | Medulla |
The spinal cord develops from the neural tube.
A few specialized cells from the neural plate form the neural crest. The neural crest gives rise to primary sensory neurons, postganglionic autonomic neurons, sensory and autonomic ganglia, melanocytes, aorticopulmonary septum, endocardial cushions, adrenal chromaffin cells in the adrenal medulla, cranial nerves, Schwann cells, pia and arachnoid mater, skull bones, pericytes, myenteric and Auerbach plexuses, odontoblasts, as well as bones and cartilages derived from the pharyngeal arches.