Fallopian tubes
Fallopian tubes
Also called the uterine tubes, they open into the uterus at one end and lie close to the ovaries at the other. Anatomically, each tube is divided into:
- An intramural segment that passes through the uterine wall
- A narrow isthmus (high risk of rupture in an ectopic pregnancy)
- The widest and longest segment, the ampulla (site of fertilization)
- A fimbriated infundibulum that lies close to the ovary
The mucosa is lined by epithelium containing:
- Ciliated cells that beat toward the uterus
- Nonciliated secretory cells
The smooth muscle is arranged in two layers:
- Inner circular
- Outer longitudinal
Peristaltic movements help move the embryo toward the uterus. The ampulla is the most common location for an ectopic pregnancy.
Ovaries
The ovaries lie on either side of the broad ligament and are associated with the mesovarium. They are the female gonads.
The surface is covered by simple cuboidal epithelium called the surface (germinal) epithelium. Beneath this is a dense connective tissue capsule called the tunica albuginea. Deep to the tunica are:
- An outer cortex
- An inner medulla
The cortex contains stromal tissue with follicles at different stages of development. The medulla contains blood vessels, nerve fibres, and lymphatics.
The ovaries are connected to the uterus by the ovarian ligament. The suspensory ligament of the ovary (infundibulopelvic ligament) attaches the ovary to the pelvic sidewall.
Blood supply and drainage:
- The ovarian artery is a branch of the abdominal aorta. It runs in the ovarian ligament, which connects the ovary to the uterus.
- The right ovarian vein drains directly into the IVC.
- The left ovarian vein drains into the left renal vein.
The left ovarian vein is longer and is prone to compression. Compression can lead to pelvic congestion and chronic pelvic pain. The left iliofemoral vessels are the most common site of thromboembolism in pregnant patients.
Breast
The breast is an accessory organ of the female reproductive system. It lies over the pectoralis major and serratus anterior muscles and is covered by skin. It is attached to the underlying muscle and the overlying dermis by the suspensory ligaments of Cooper.
Superolaterally, breast tissue extends into the axilla as the axillary tail of Spence. Breast tissue is a mix of:
- Adipose tissue (under the influence of estrogen)
- Glandular tissue (under the influence of progesterone)
Breast size varies mainly with the amount of adipose tissue, while milk production depends on the amount of glandular tissue.
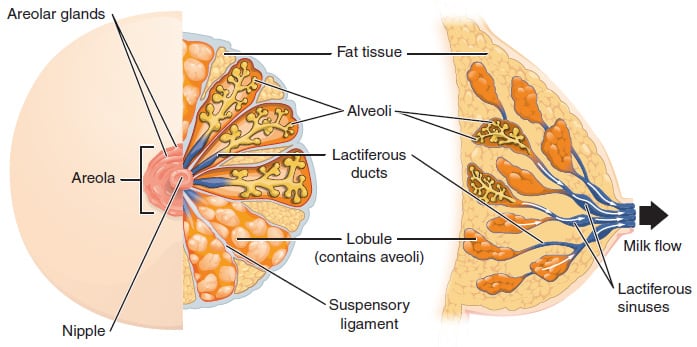
- Nipple and Areola: The pigmented nipple and areola are located anteriorly at the level of the fourth rib and are lined by lightly keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. The areola is round and contains raised sebaceous glands, which enlarge during pregnancy to form the tubercles of Montgomery. The nipple lacks sebaceous glands. The lactiferous ducts open onto the surface of the nipple in a ring-like fashion. Smooth muscle fibres lie beneath the nipple-areolar complex and are arranged in radial/longitudinal and circular directions. The circular fibres are called the muscle of Sappey, while the radial fibres form the muscle of Meyerholz. Contraction of these muscles during breast feeding results in the ejection of milk.
- Mammary Gland: The mammary gland is a modified sweat gland. The glandular tissue is divided into lobes made of clusters of milk-producing alveoli. Myoepithelial cells surround the alveoli. The lobules drain first into intralobular ducts, then into interlobular ducts, which eventually drain into the lactiferous ducts. There are 15-20 lactiferous ducts in total. Each duct dilates toward the areola to form a lactiferous sinus, which acts as a temporary reservoir for milk. The upper outer quadrant of the breast is the major site for breast cancer because it is rich in glandular tissue.
- Blood Supply: The major supply is from the internal mammary (internal thoracic) artery. Other sources include the thoracoacromial artery, lateral thoracic artery, vessels to serratus anterior/thoracodorsal artery, and terminal branches of the third to eight intercostal perforators. Venous drainage is divided into a superficial system (plexus of Haller) and a deep system.
- Lymphatic drainage: Superficial lymphatics from the nipple and areola form Sappey’s plexus, which eventually drains into the axillary nodes. This plexus also communicates with the deep lymphatics. Most of the breast parenchyma drains to the axillary nodes. The remaining drainage goes to the internal mammary (parasternal) nodes, followed by the posterior intercostal nodes. Some lymphatics located more cranially may drain into the supraclavicular lymph nodes in the cervical group. Lymphatics also communicate with the opposite breast and with subdiaphragmatic and hepatic nodes.
- Nerve Supply: Nipple sensation is carried by the lateral cutaneous branch of T4. Sensation to the rest of the breast is from the T3-5 intercostal nerves. The upper and lateral part is also supplied by the supraclavicular branch of the cervical plexus.