The endocrine system is made up of multiple glands that work together to maintain homeostasis in the body. The hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas, and adrenal glands are the major components of the endocrine system. In addition, adipose tissue has recently been recognized as an endocrine organ with important roles in health and disease.
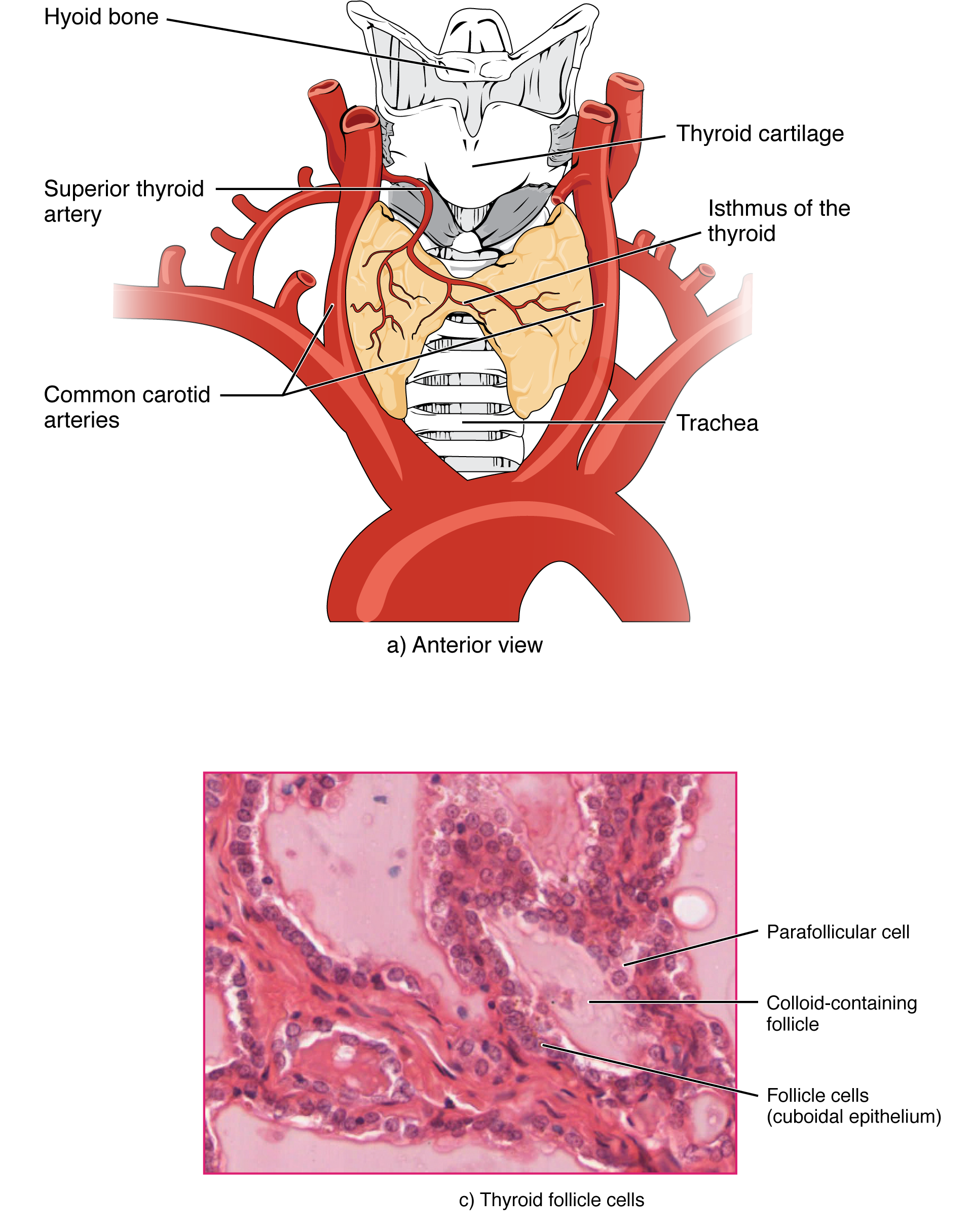
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located anterior to the trachea in the neck. It has two lobes connected by an isthmus.
The thyroid is attached to the cricoid cartilage by the suspensory ligament of Berry. The pretracheal fascia covers the thyroid gland as well as the thyroid and cricoid cartilages and the hyoid bone. Because of this fascial attachment, the thyroid gland moves upward with swallowing or with protrusion of the tongue.
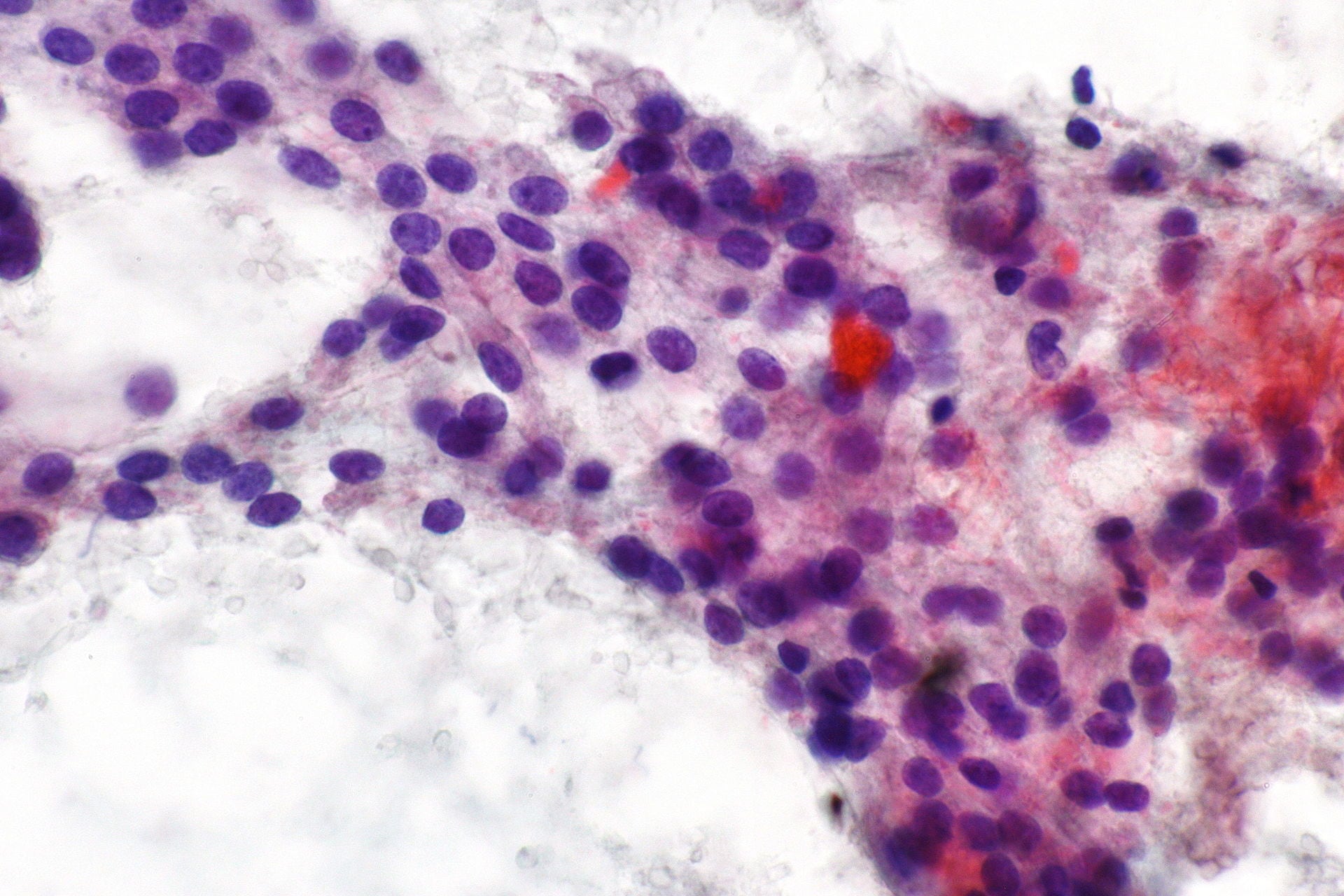
Histologically, the thyroid gland contains multiple follicles filled with colloid.
In an active gland, you see smaller follicles, taller columnar-appearing cells with prominent Golgi and endoplasmic reticulum, and less colloid.
Colloid consists of glycoproteins such as iodinated thyroglobulins, which are made and secreted by follicular cells.
Parafollicular © cells are interspersed between the epithelial cells. They appear pale with clear cytoplasm and are seen only in the middle third or lateral lobes of the thyroid. Parafollicular cells secrete calcitonin.
Blood supply comes from the superior and inferior thyroid arteries, and in some cases from the thyroidea ima artery.
The superior and inferior thyroid arteries anastomose with each other on the posterior margin of the gland.
The thyroidea ima is a direct branch of the arch of the aorta or, sometimes, the brachiocephalic trunk.
Venous drainage occurs through three pairs of veins.
The right and left inferior thyroid veins communicate in front of the trachea and may be injured during a tracheostomy.
Lymphatic drainage from the upper part goes to the jugulodigastric nodes in the deep cervical chain, and from the lower part to the jugulo-omohyoid nodes. Some lymph drains directly into the thoracic duct, while a few channels drain to the brachiocephalic nodes in the mediastinum. Prelaryngeal and pre- and paratracheal nodes are intermediary nodes in the lymphatic drainage of the thyroid gland.
The parathyroid glands are located behind the thyroid gland, embedded in the fascial capsule of the thyroid. They produce PTH or parathyroid hormone.
There are four parathyroid glands: two superior and two inferior.
Histologically, the parathyroid contains mainly two cell types: chief (principal) cells and oxyphil cells.
The parathyroid glands are supplied by the parathyroid artery, which arises from the inferior thyroid artery. Venous and lymphatic drainage follows the thyroid gland.
Sign up for free to take 4 quiz questions on this topic