Leukemias
Leukemia is a malignant clonal proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow.
- Acute leukemias are characterized by predominantly immature (blast) cells in the bone marrow and blood.
- Chronic leukemias show predominantly mature-appearing cells.
Based on the cell lineage of origin, leukemias are classified as:
- Myeloid
- Lymphoid
All leukemias and lymphomas are monoclonal in origin (they arise from a single precursor or “mother” cell). In contrast, leukocytosis due to infection is polyclonal.
Characteristic features of common leukemias
| Type | Features |
| ALL (acute lymphoblastic leukemia) | Most common in childhood; presents with fever, bleeding, musculoskeletal pain, hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy; CNS involvement common |
| AML (acute myeloid leukemia) | Most common acute leukemia in adults; presents with fever, fatigue, weight loss, anemia, bleeding, leukostasis; Auer rods seen; mutations seen in FLT3, NPM1, DNMT, IDH, NRAS, RUNX1 genes; bad prognosis |
| CML (chronic myeloid leukemia) | More common in adults; some may be asymptomatic; splenomegaly; associated with Philadelphia chromosome (BCR-ABL1 fusion gene) that produces excess tyrosine kinase |
| CLL (chronic lymphocytic leukemia) | Most common in adults >65 years of age; commonly asymptomatic; lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly; good prognosis; may be preceded by monoclonal B cell lymphocytosis |
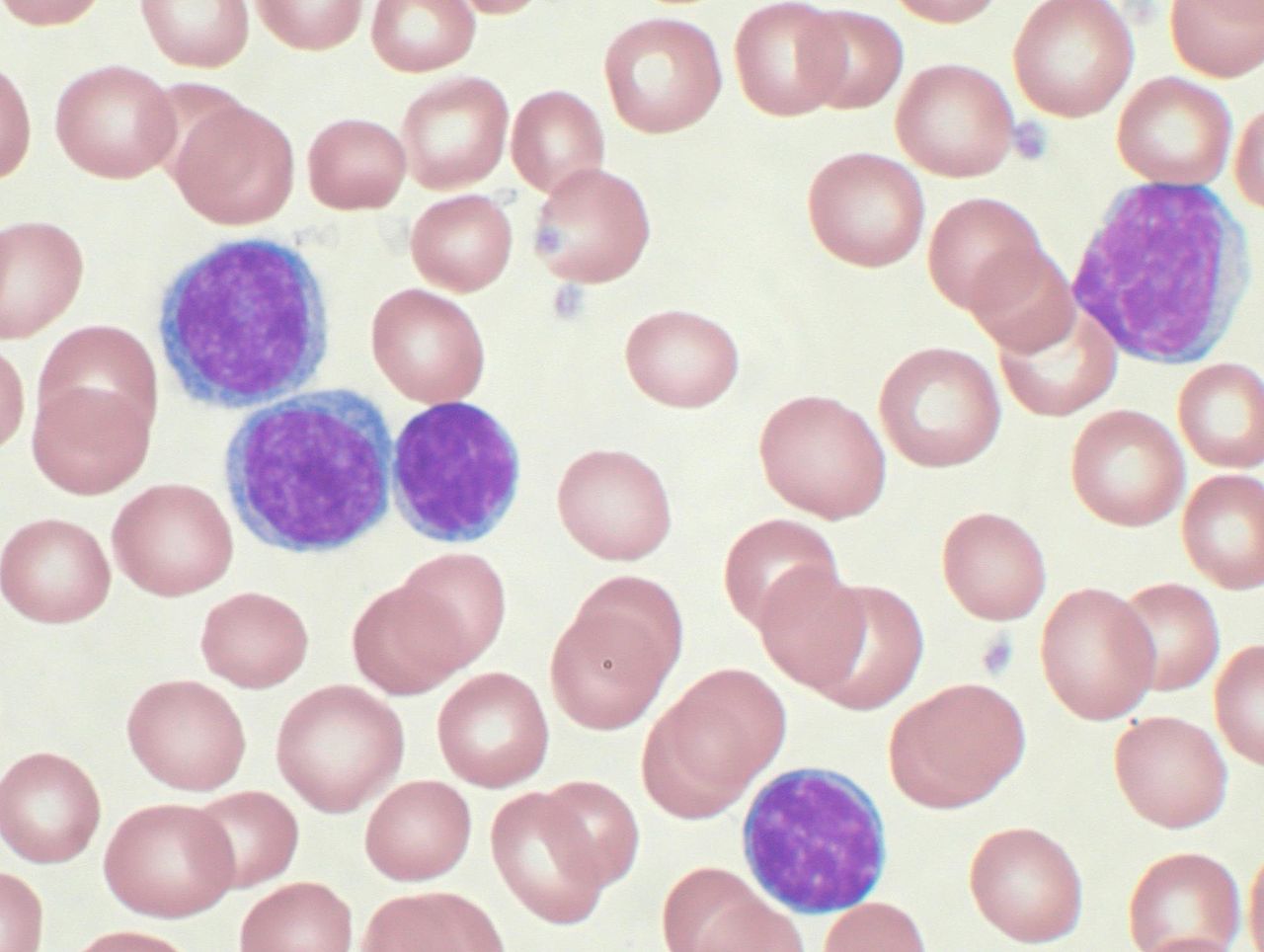
High-power magnification (1000 X) of a Wright’s stained peripheral blood smear showing chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). The lymphocytes with the darkly staining nuclei and scant cytoplasm are the CLL cells.
Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): A subset of AML caused by t(15;17), which creates an abnormal gene PML/RARa. This leads to uncontrolled proliferation of promyelocytes. It can be treated with all-trans retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide. It predisposes to DIC.
Hairy cell leukemia: A type of CLL characterized by hairlike cytoplasmic projections from neoplastic B cells. It’s more common in older males. Hairy cell leukemia is associated with BRAF or MAP2K1 mutations. It presents with fatigue, fever, weight loss, splenomegaly, easy bruising, hepatomegaly, etc. Treatment is with cladribine, pentostatin, alpha-interferon, or splenectomy.
Risk factors for leukemias:
- Exposure to herbicide agent orange (used in Vietnam war) can cause CLL.
- Down’s syndrome and neurofibromatosis are associated with an increased risk of ALL and AML.
- Radiation exposure (including cancer therapy) increases risk for ALL, AML, and CML.
- Benzene exposure is a risk factor for AML.
- Pesticides are a risk factor for ALL.
- MDS, essential thrombocythemia, and polycythemia vera can lead to AML.
Diagnosis of leukemias:
- WBC count may be normal in leukemia.
- A highly elevated WBC count > 100,000/microl is typically seen in CML and CLL.
- Acute leukemias may show leukocytosis or leukopenia, blast cells, and may be accompanied by anemia or thrombocytopenia.
- Myeloid blasts (compared with lymphoid blasts) are larger, have more abundant cytoplasm, and may show Auer rods.
- The Philadelphia chromosome can be detected by cytogenetic or molecular testing in CML. Some cases of ALL will be positive for the Philadelphia chromosome as well.
- Flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and cytochemistry can be used to determine cell lineage.
- CD3+ cells are T-cell lineage.
- CD19+, CD22+, CD10+, CD79+ cells are B-cell lineage.
- Most ALL cases are MPO negative and TdT +.
- CD34+ blast cells in AML and ALL are associated with bad prognosis.
- CLL cells are CD5+, CD19+, and CD23+ and will have either kappa or lambda light chain.
- CD38+ and ZAP-70 + CLL have a worse prognosis.
- Serum uric acid levels are high due to rapid cell growth and accelerated cell breakdown after chemotherapy.
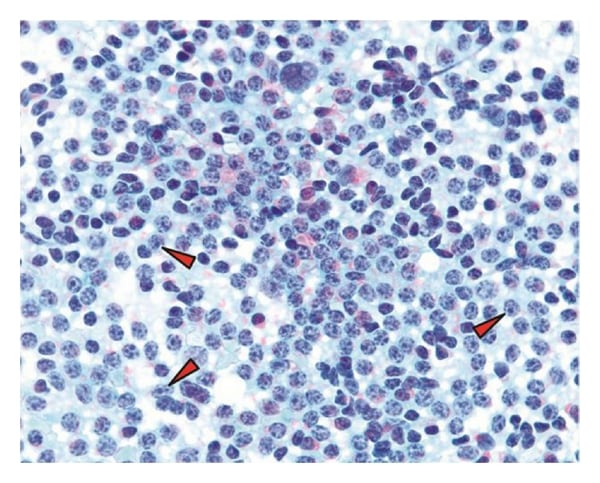
Peculiar chromatin distribution and presence of numerous prolymphocytes (red arrowheads) with increased cell density. Note the coarse distribution of the chromatin and tinctorial quality of the nucleoli in the prolymphocytes in this stain.
Characteristic bone marrow and peripheral smear findings in leukemias
| Type | Findings* |
| ALL | >20% lymphoblasts in bone marrow and peripheral smear |
| AML | >20% blast cells in the bone marrow; karyotype anomalies common in blast cells; cytochemical stains varies according to class; Pelger-Huet anomaly; sometimes “dry tap” due to increased reticulin in bone marrow |
| CML | Chronic phase: <10% myeloblasts in blood and bone marrow; basophilia; Accelerated phase: 10-20% myeloblasts in blood and bone marrow; marrow basophils >20%; thrombocytopenia; Blast crisis: >20% myeloblasts in blood and bone marrow; Reduced neutrophil alkaline phosphatase |
| CLL | >30% normal-looking lymphocytes in bone marrow; “Smudge cells” or “basket cells” are seen on peripheral smear |
*bone marrow will be typically hypercellular in all leukemias.
Treatment: Adolescent survivors of leukemia should be followed up for osteonecrosis and adverse effects of chemotherapy and radiotherapy, such as cardiac failure, endocrine dysfunction, ILD, and other types of leukemia like AML.
Treatment for leukemias
| Type | Treatment |
| ALL | Imatinib, Dasatinib, Nilotinib; immunotherapy with CAR (chimeric antigen receptor) T cells using patient’s own T cells |
| AML | Induction therapy with anthracyclines plus cytarabine; fludarabine, granulocyte CSF, idarubicin, stem cell transplant; rarely radiation; enasidenib for IDH2 mutations; |
| CML | Tyrosine kinase inhibitors like imatinib; allogenic bone marrow transplant; chemotherapy with busulfan, cyclophosphamide, hydroxyurea; less commonly radiotherapy |
| CLL | Watchful waiting for asymptomatic patients; treatment needed only in worsening thrombocytosis, thrombocytopenia, anemia, progressive lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, or constitutional symptoms; drugs like ibrutinib, idelalisib, ofatumumab, rituximab, immunotherapy, CAR-T cell therapy, radiotherapy, BMT; chemotherapy like fludarabine, cladribine, cyclophosphamide, and pentostatin can be used. |