Blood cell lineages
Before birth, hemopoiesis occurs primarily in the liver and spleen. Some cells also develop in the thymus, lymph nodes, and red bone marrow. After birth, most blood cell production is limited to red bone marrow in specific regions, although some white blood cells are produced in lymphoid tissue.
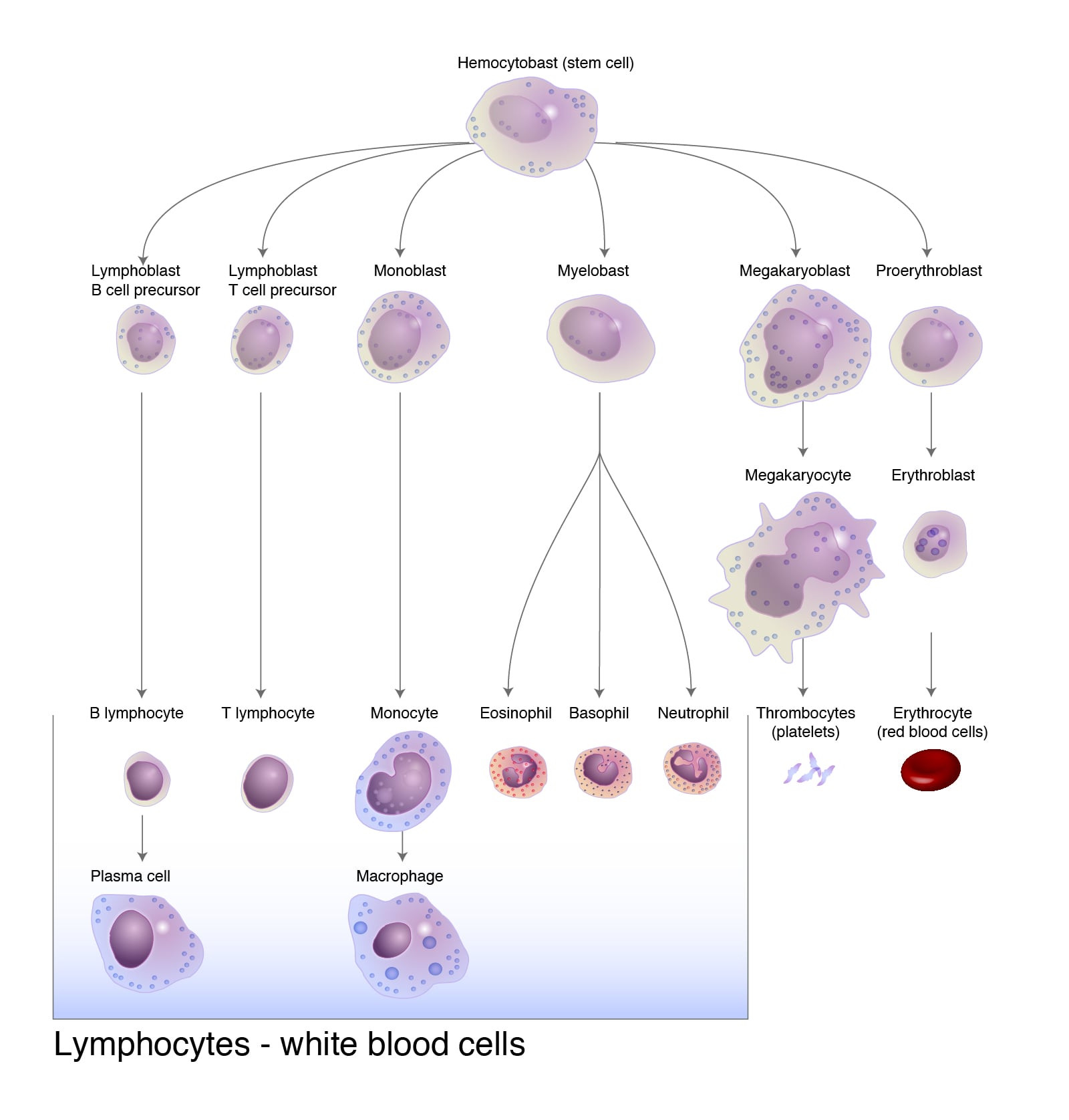
All types of formed elements develop from a single cell type: the stem cell (pluripotent cells or hemocytoblasts). Seven different cell lines develop from the hemocytoblast, and each line is controlled by a specific growth factor.
Hemocytoblasts can give rise to either myeloid or lymphoid lineages:
- Lymphoid lineage cells include T, B, and natural killer (NK) cells.
- Myeloid lineage cells include megakaryocytes, erythrocytes, granulocytes and macrophages (GM).
Common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs) can differentiate into all types of lymphocytes. Common myeloid progenitors (CMPs) can give rise to all classes of myeloid cells. Dendritic cells can arise from either CLPs or CMPs.
Megakaryocytes give rise to platelets. Granulocytes include neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils and have cytoplasmic granules. Lymphocytes and monocytes are agranulocytes.
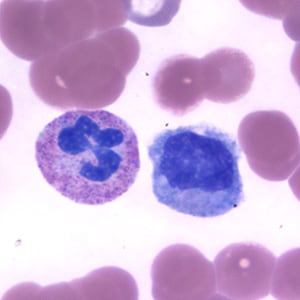
Neutrophil (left) and monocyte (right) in a thin blood smear, stained with Giemsa.
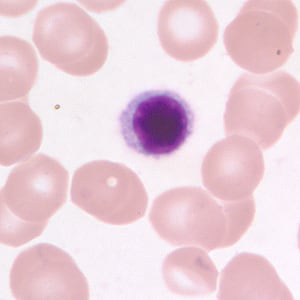
Small lymphocyte in a thin blood smear, stained with Giemsa