Cholangitis
Primary biliary cirrhosis or primary biliary cholangitis: This is an autoimmune, chronic, progressive disorder that is more common in women. It is characterized by inflammation and scarring of the intrahepatic bile ducts. It typically presents with jaundice, pruritus, abdominal pain, and fatigue. Complications include portal hypertension, fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies, osteoporosis, and cirrhosis. Other autoimmune disorders may be associated.
Hypercholesterolemia can occur due to biliary stasis. Most patients are positive for antimitochondrial antibodies, such as PDC-E2 (pyruvate dehydrogenase). A past bacterial or viral infection can act as a trigger.
Diagnosis is based on:
- Elevated direct bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, GGT, AST, and ALT
- Positive antimitochondrial antibodies
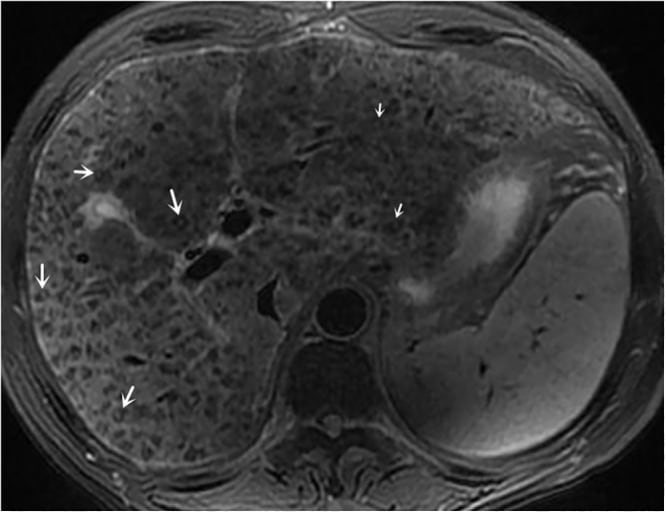
- MRI findings, including a periportal halo sign, lymphadenopathy, and increased signal intensities in the liver
Treatment includes ursodeoxycholic acid or obeticholic acid, cholestyramine for pruritus, fibrates, and liver transplant.
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC): This disorder is characterized by inflammation and scarring (sclerosis) of the bile ducts, involving both intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts. It is more common in men. It can present with fatigue, pruritus, jaundice, and splenomegaly. It can also lead to fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies, osteoporosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure.
About 70% of patients with PSC have IBD, most commonly ulcerative colitis. PSC has also been associated with autoimmune disorders such as type 1 diabetes mellitus, celiac disease, RA, and Grave’s disease. It is strongly associated with HLA A1, B8, DR6, and DR3. There is an increased risk of choledocholithiasis and cholangiocarcinoma.
Laboratory findings include elevated AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase, gamma glutamyl transpeptidase, gamma globulins (raised IgM), and elevated direct bilirubin. pANCA, anti-smooth muscle antibodies, ANA, and anticardiolipin antibodies may be positive.
Imaging studies include MRCP, ERCP, and PTC (percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography). Imaging shows multiple strictures and dilations, producing a beaded appearance. Biopsy shows characteristic onion-skin (concentric) fibrosis.
Treatment includes cholestyramine for pruritus, ursodeoxycholic acid, endoscopic balloon dilation of bile ducts, supportive therapy, and definitive treatment with liver transplantation.