Poxviruses
This family includes Molluscum contagiosum virus, vaccinia virus, and smallpox virus. For the USMLE, Molluscum contagiosum virus is the most important.
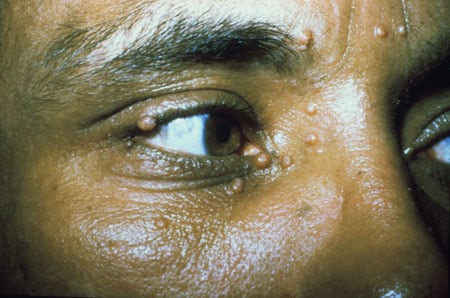
Molluscum contagiosum virus
Molluscum contagiosum virus causes umbilicated lesions on the skin and mucosa. It most often affects children and immunocompromised individuals; in immunocompromised patients, the disease can become generalized.
It spreads through close contact. Diagnosis is usually clinical. On biopsy, infected cells show cytoplasmic inclusions.
Smallpox and vaccinia virus
Smallpox is also called Variola. Smallpox has been eradicated worldwide. The virus is brick-shaped. Its main importance today is its potential use as a bioterrorism agent.
Smallpox can spread easily by aerosols. It presents with fever and a maculopapular rash in a centrifugal distribution.
Vaccinia virus is a nonpathogenic poxvirus used for experimental and research purposes.