All triangles share a few geometric rules. First, the angles in any triangle add up to 180 degrees. In other words, the three interior angle measures must sum to . Second, the area of any triangle is one-half the product of its base and its height:
.
Sometimes you’ll be given three side lengths and asked whether they can form a triangle. To decide, use the triangle inequality theorem.
To apply it, add the two smaller side lengths and compare the sum to the largest side length:
Let’s do a quick example.
Do the three following side lengths make a triangle?:
The sum of and needs to be larger than . We can write this as:
So these side lengths do form a triangle. An example of side lengths that do not form a triangle is , , and because , which is smaller than .
There are also a few extra rules that apply only to certain types of triangles. These are examined below.
Equilateral triangles have all three sides equal and all three angles equal. So, if you’re missing any side lengths or angle measures, remember that they are all the same in an equilateral triangle.
These triangles have two sides equal and two angles equal. So, if you know one of the equal sides, you know the other as well. The same is true for the equal angles.
A common isosceles-triangle problem is finding all the angle measures when you’re given just one angle. Since the sum of the angles is 180º, you can solve for the remaining angles using that total and the fact that two angles are equal. This is why it’s important to notice when a problem tells you a triangle is isosceles.
Scalene triangles are often the most challenging to work with because there are no equal sides or equal angles. Problems involving scalene triangles often include multiple triangles that are related in some way. This relationship may include congruency or similarity.
When comparing two triangles, pay attention to what they have in common.
If two parts of a triangle are congruent, this is shown with identical hatch marks, like below:
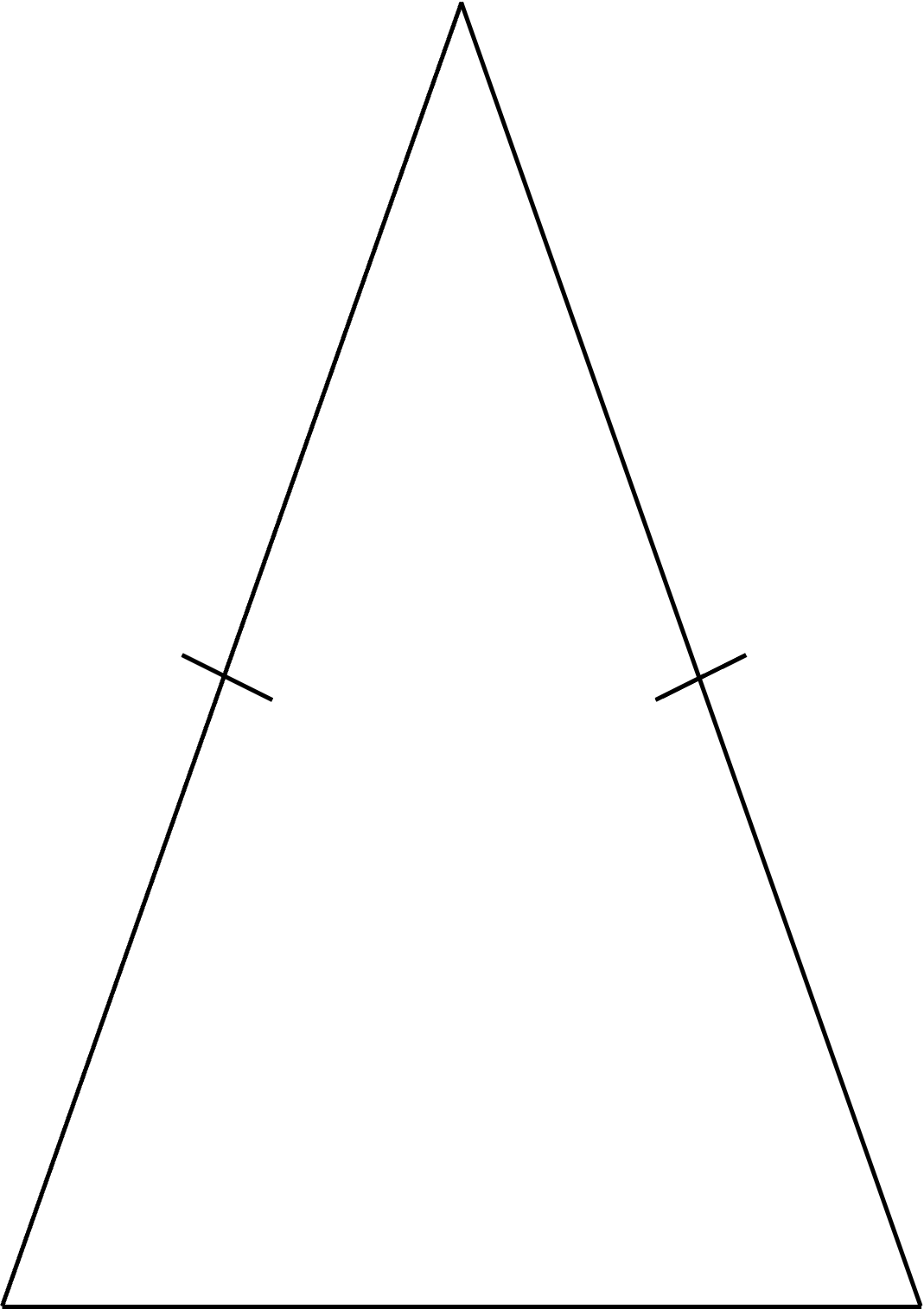
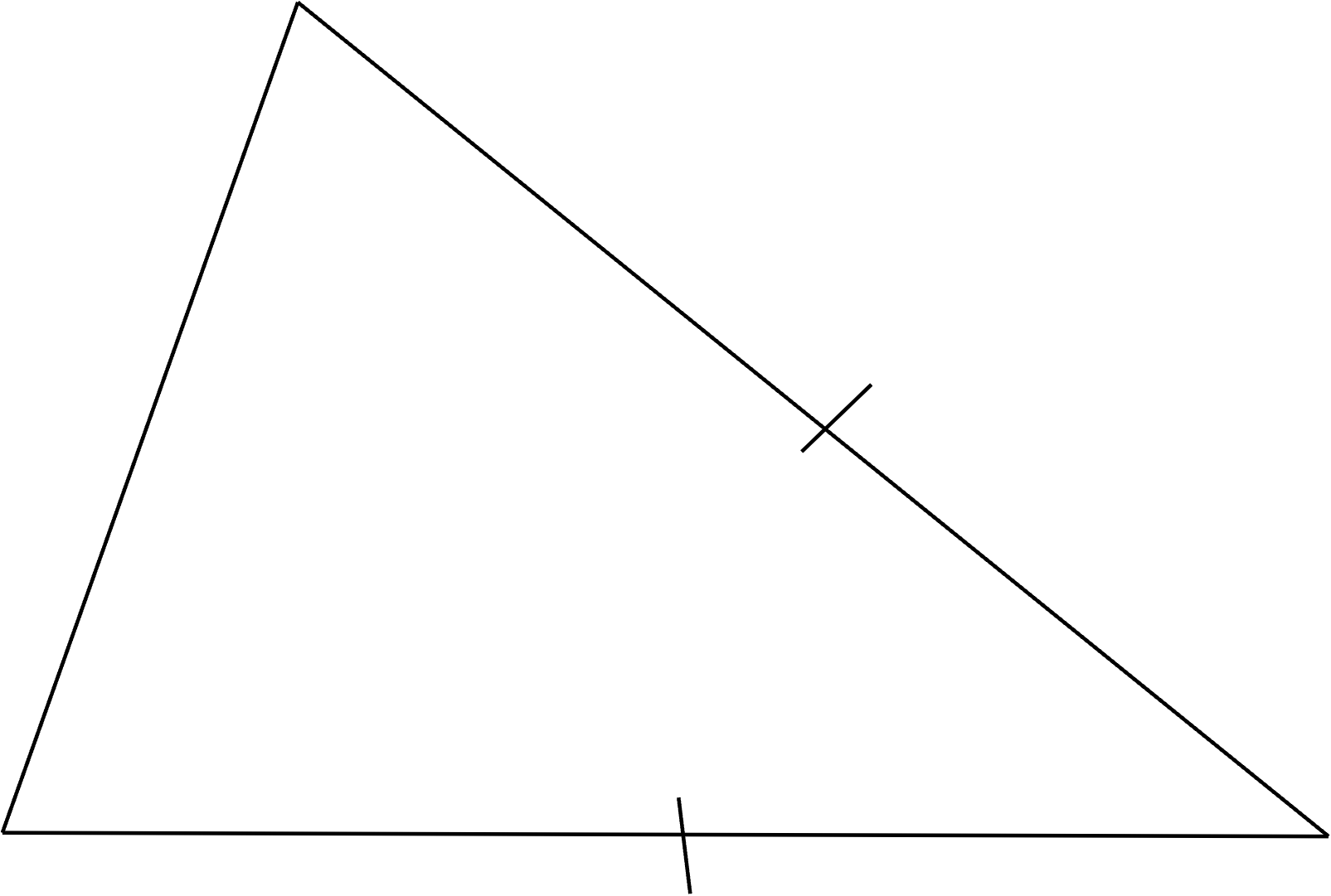
Two different triangles can also share congruent parts. The same hatch-mark notation is used:

Let’s do an example involving congruent angles. If the measure of angle is 50º, find the angle measure in the triangles below:
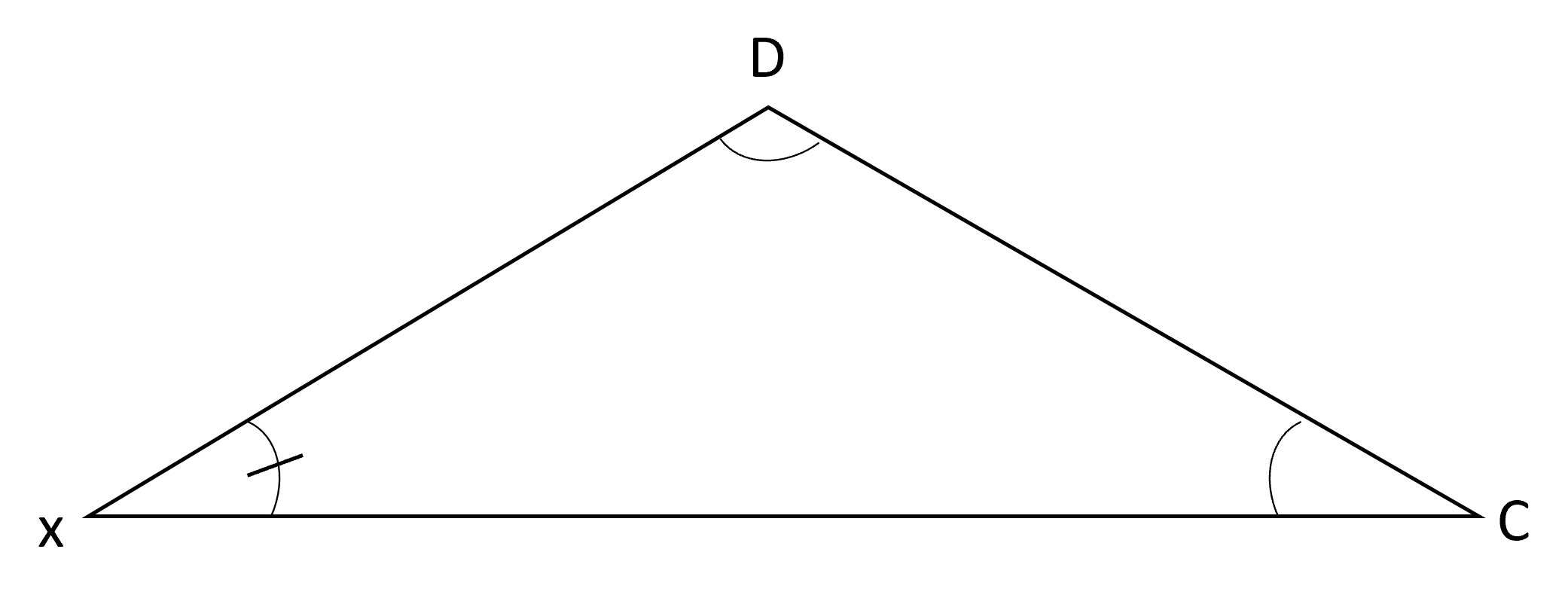
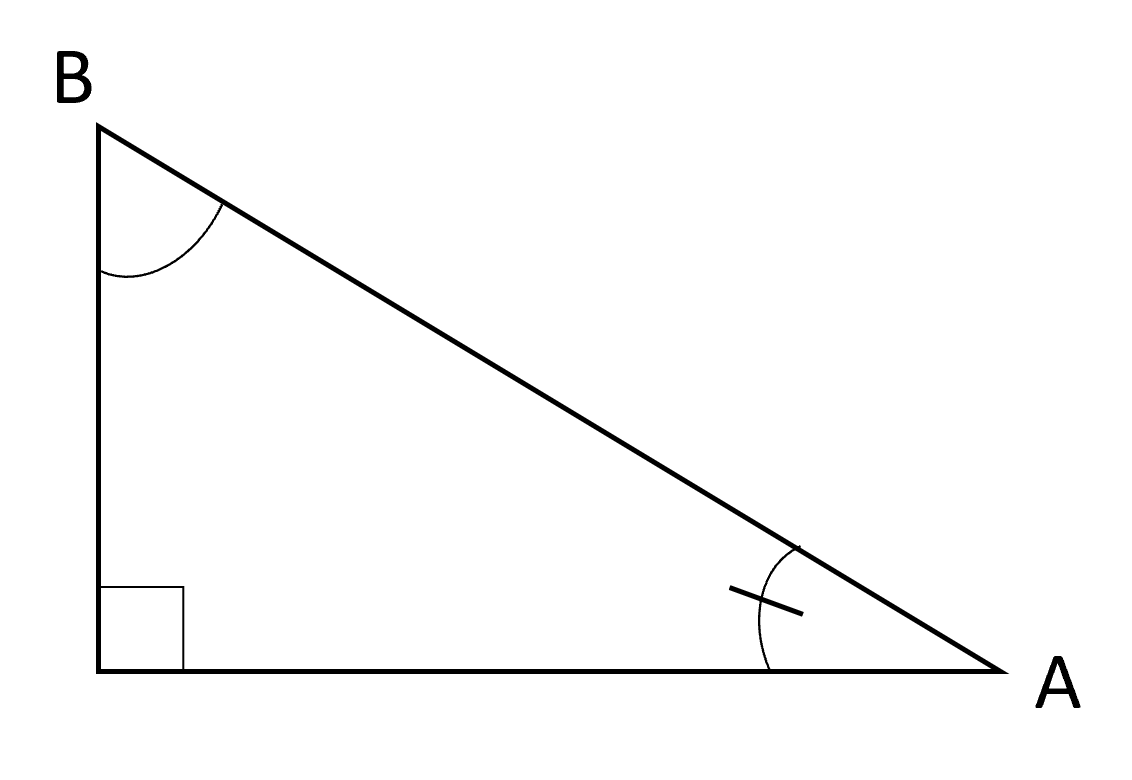
First, find the measure of the angle in the first triangle that is congruent to an angle in the second triangle. That shared angle is what connects the two triangles.
Use the fact that the angles in a triangle sum to 180º:
Since angles and are congruent,
The measure of angle is 40º.
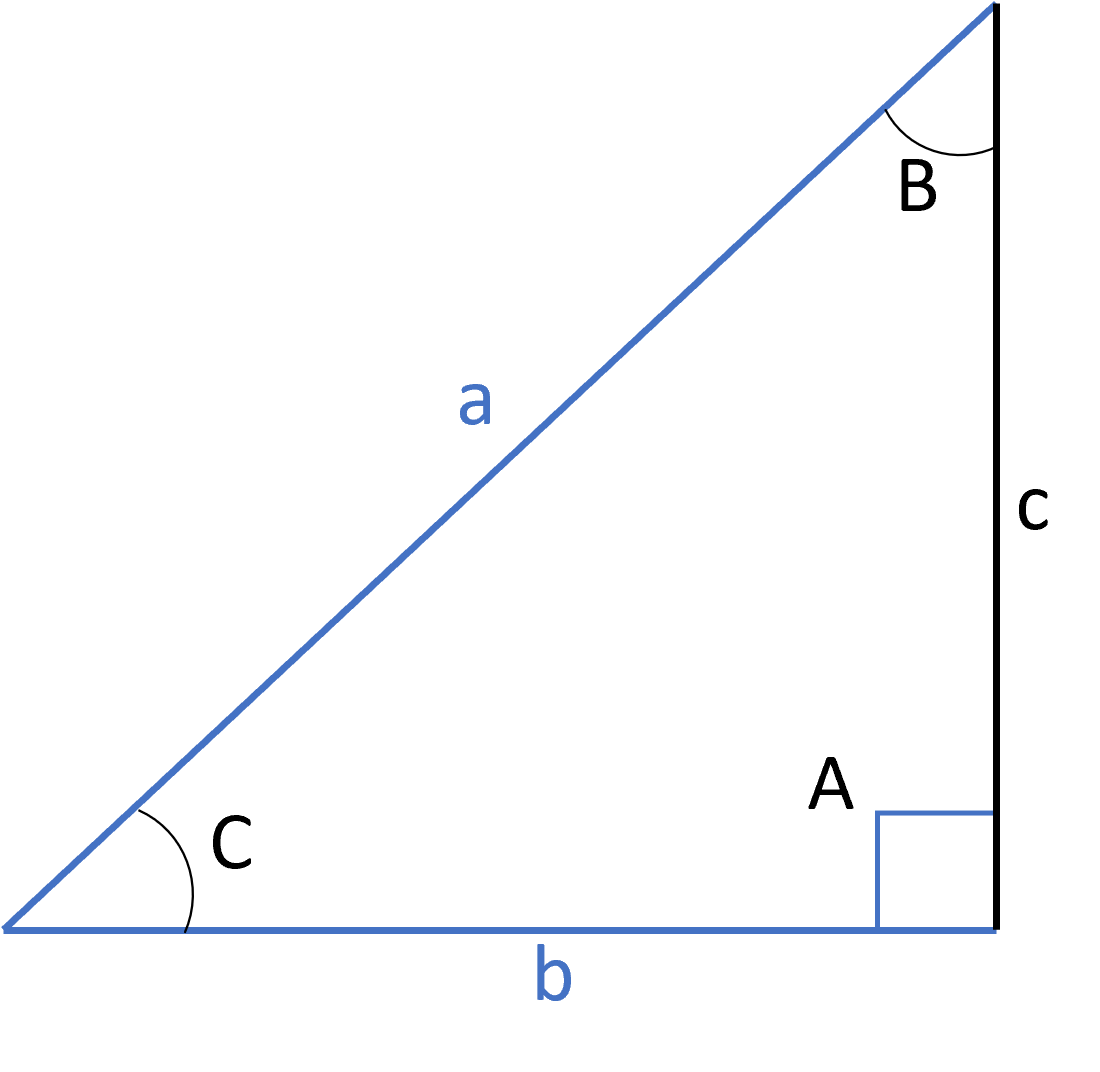
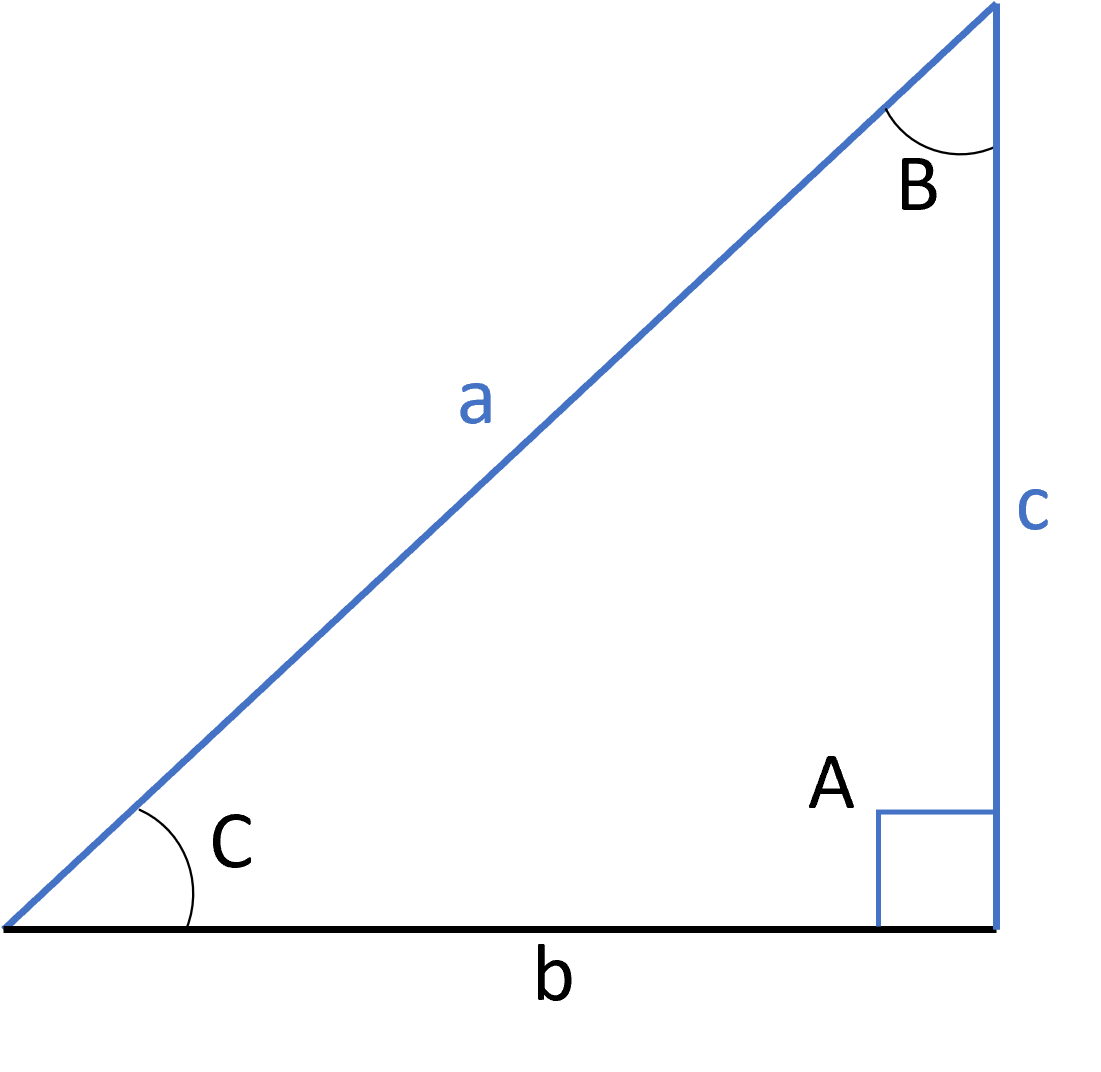
Two triangles are not always congruent just because they share a few matching parts. To prove two triangles are congruent, you can use specific congruency tests.
If two triangles share the same blue characteristics for a single test listed below, then they are congruent. If none of the tests apply, then you cannot conclude the triangles are congruent. The angles and sides listed for each test refer to the matching parts between the two triangles.
The blue lines in the images below show which parts you compare.
All three sides are equal:
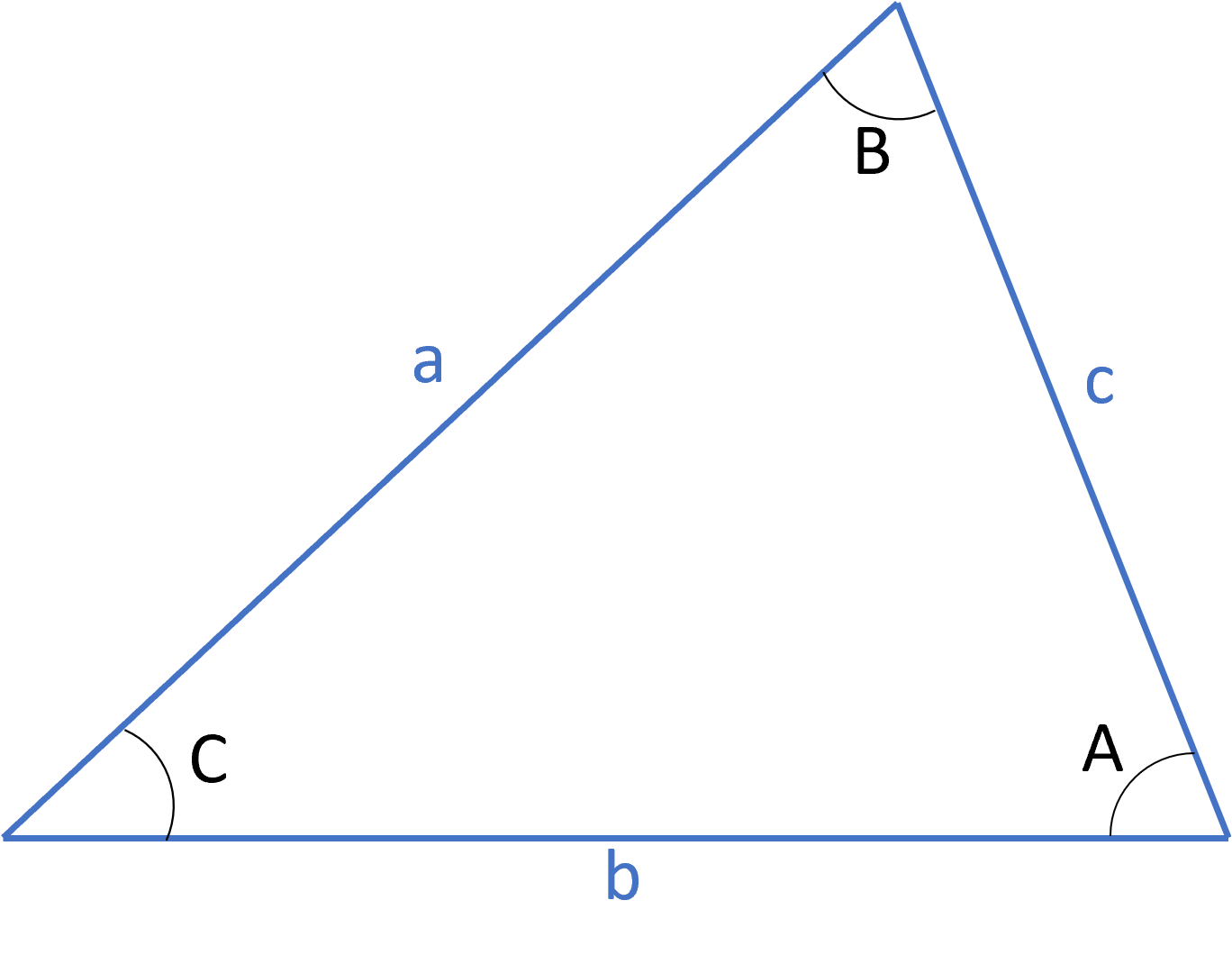
A side, the included angle, and another side (in that order) are equal:
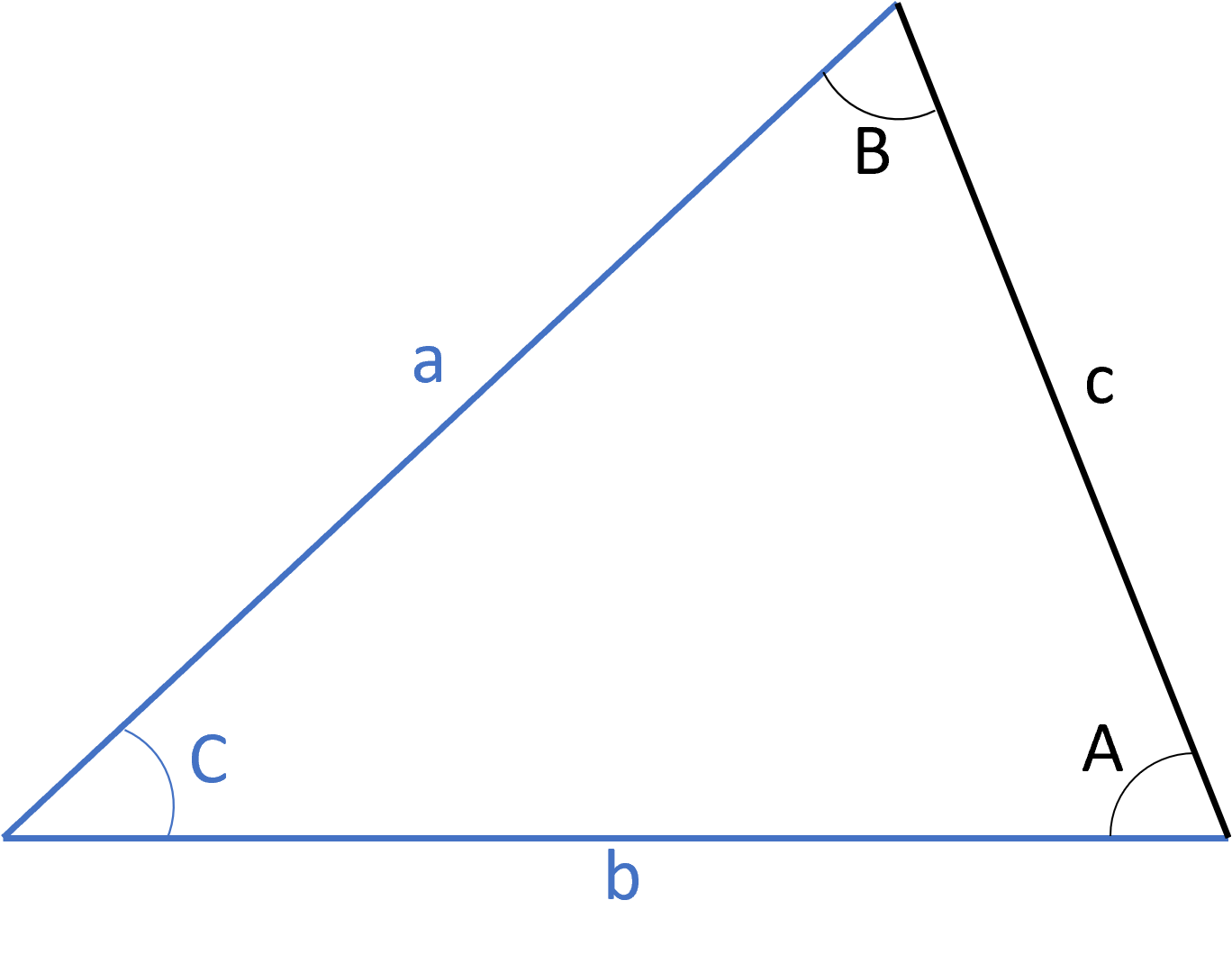
An angle, the included side, and another angle (in that order) are equal:
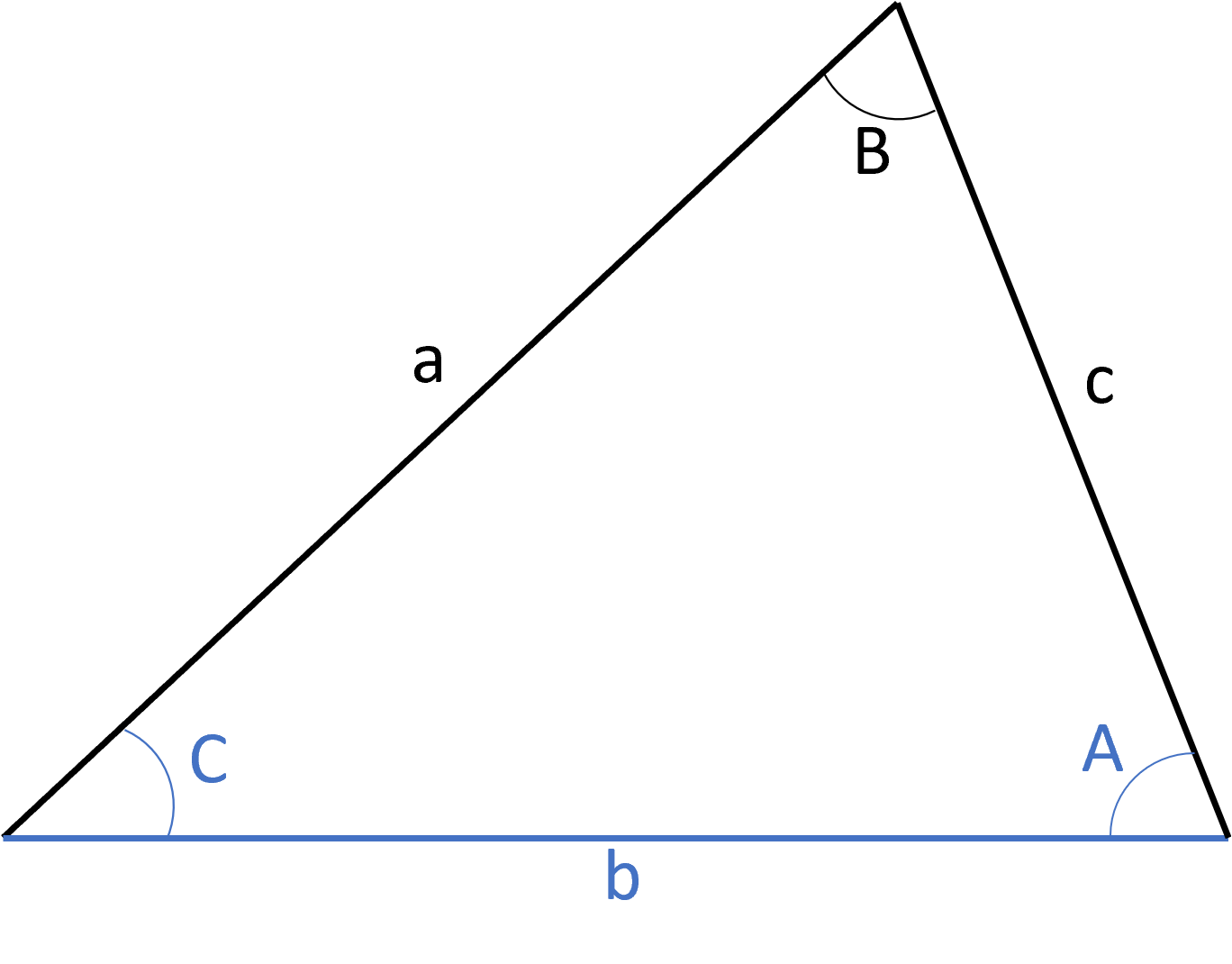
An angle, another angle, and a side (in that order) are equal:
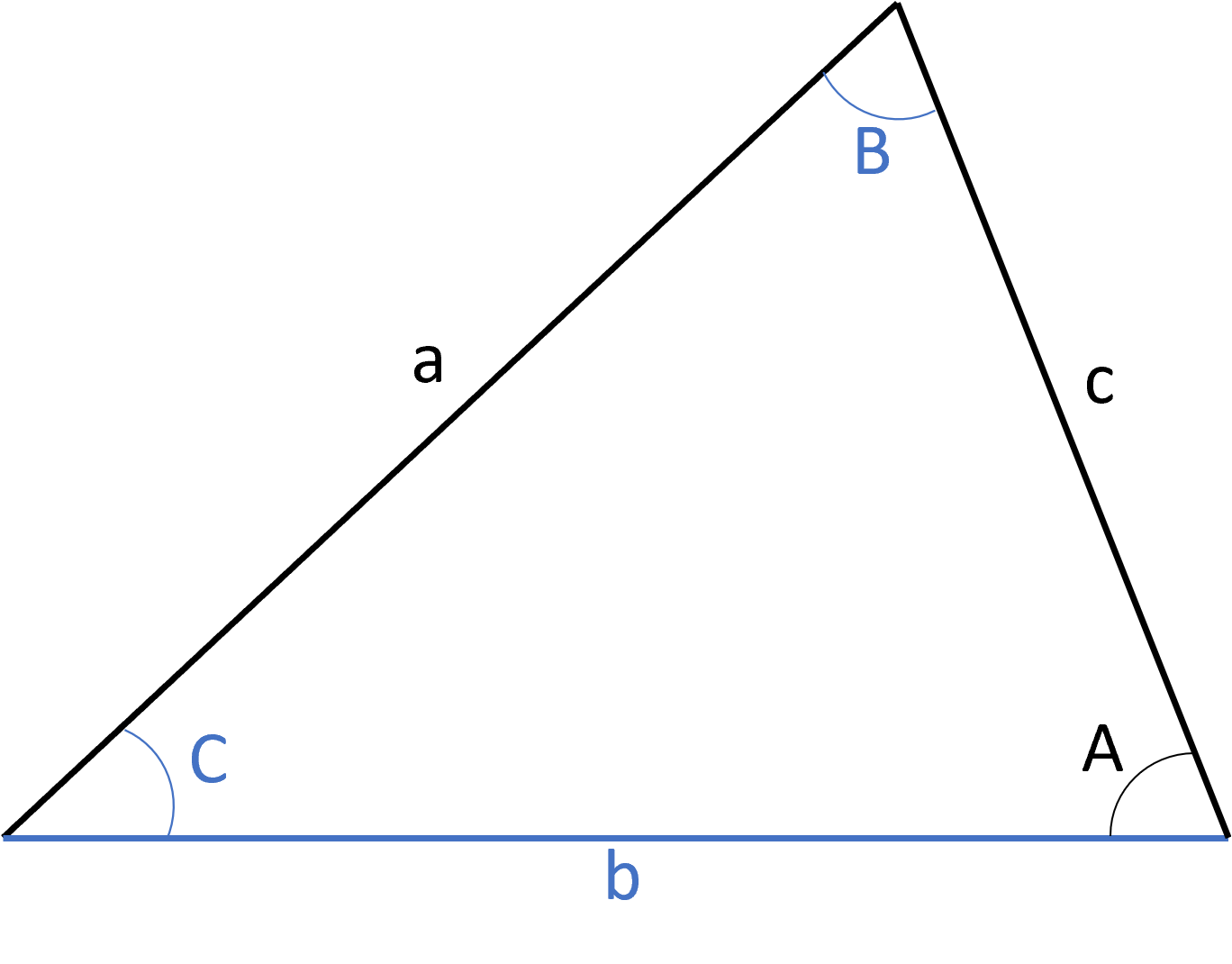
The hypotenuse, the right angle, and one side (it doesn’t matter which of the two non-hypotenuse sides) are equal:
If two triangles are similar, the problem may state it directly, or you may be able to tell because the triangles have equal angle measures.
Knowing triangles are similar is useful because it lets you find unknown side lengths using proportions. For example, in the similar triangles below, you can solve for by setting up a proportion between corresponding sides:
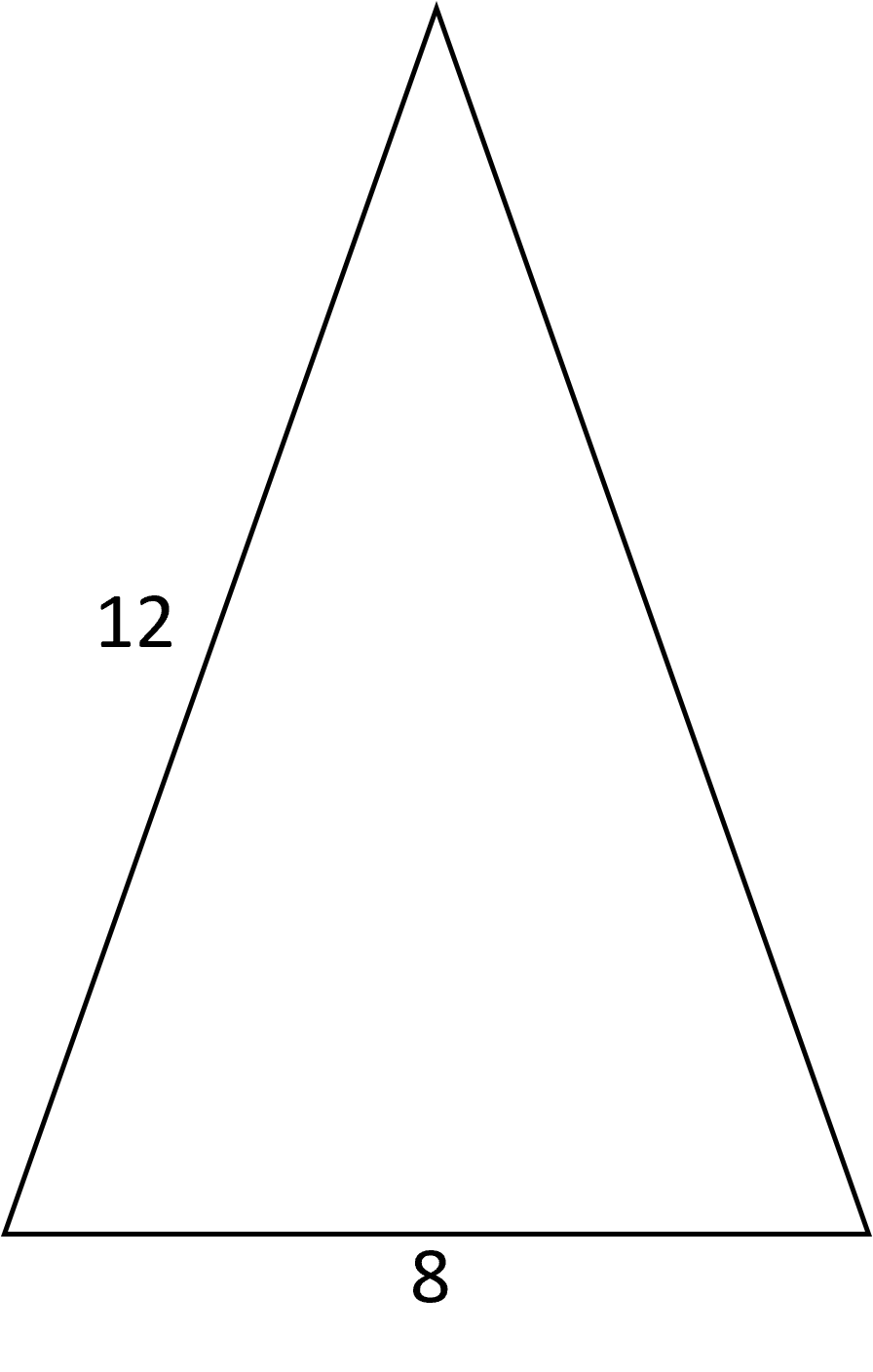
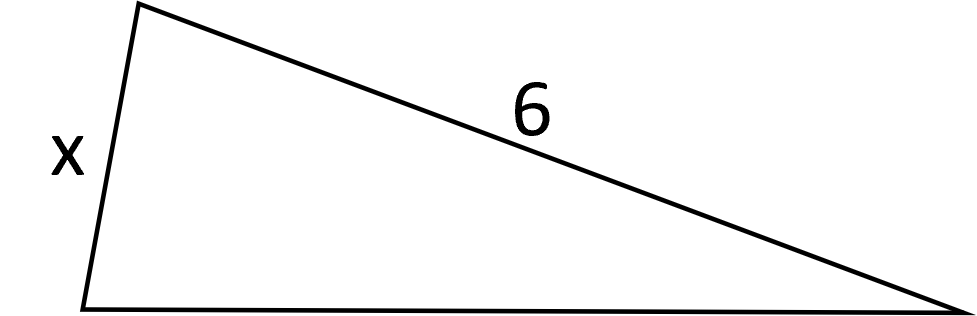
We see that the long side of the smaller triangle is half the length of the long side of the larger triangle. Because these triangles are similar, the proportion of the larger triangle to the smaller triangle is . Now solve for using a ratio:
The value of the side in the above example of similar triangles is .
Sign up for free to take 4 quiz questions on this topic