HAART (highly active antiretroviral therapy): HAART is a combination of three or more antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV infection. The main goal of HAART is to prevent the development of antiviral-resistant strains and to increase treatment efficacy.
| Drug and class | Mechanism of action | Adverse effects |
| Nucleoside or nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors or NRTIs: Abacavir, didanosine, lamivudine, stavudine, zidovudine and tenofovir | Nucleoside or nucleotide analogues that inhibit the viral reverse transcriptase enzyme and viral replication. These drugs must be activated by phosphorylation via cellular kinases. Zidovudine is an analogue of thymidine; emtricitabine and lamivudine are analogues of cytidine; abacavir is an analogue of deoxyguanosine; tenofovir (a prodrug) is an analogue of adenosine. | Peripheral neuropathy, lactic acidosis, myelosuppression, anemia, lipodystrophy, renal failure. Tenofovir may decrease bone mineral density. Abacavir may cause hypersensitivity reactions. Didanosine may cause pancreatitis and hepatomegaly. |
| Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors or NNRTIs: Nevirapine, efavirenz, delavirdine, rilpivirine | Bind to viral reverse transcriptase at a site different from the nucleoside binding site, causing allosteric inhibition of reverse transcriptase. | Skin rash, SJS, hepatitis, hepatic failure, prolongation of QTc, cyt P450 interactions. Efavirenz causes delusions, psychosis, vivid dreams, and mania. |
| Protease inhibitors or PIs: indinavir, darunavir, atazanavir, nelfinavir, lopinavir etc. | Inhibit HIV protease, which is essential for viral maturation and cleavage of gag/pol. | Metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, lipodystrophy, dyslipidemia, CAD, stroke. Atazanavir has fewer adverse effects on carbohydrate metabolism. Indinavir and saquinavir may cause nephrolithiasis. |
| Integrase inhibitors: dolutegravir, elvitegravir and raltegravir | Prevent the formation of covalent bonds between viral and host DNA, thereby inhibiting integration of viral DNA into host DNA. | Dizziness, depression, sleep disorders, myopathy, rhabdomyolysis. Dolutegravir causes renal failure and may cause neural tube defects. |
| Fusion inhibitors: enfuvirtide | Bind to viral gp41 and block fusion of the viral particle with the host cell, preventing viral entry into the cell. | Peripheral neuropathy, injection site reactions |
| Chemokine receptor antagonists or CCR5 antagonists: maraviroc | Bind to the CCR5 chemokine co-receptor, blocking the interaction of viral gp120 with host cell CCR5 and preventing entry of HIV into the cell. | Dizziness, skin rashes, hepatotoxicity; use caution with cyt P450 affecting drugs |
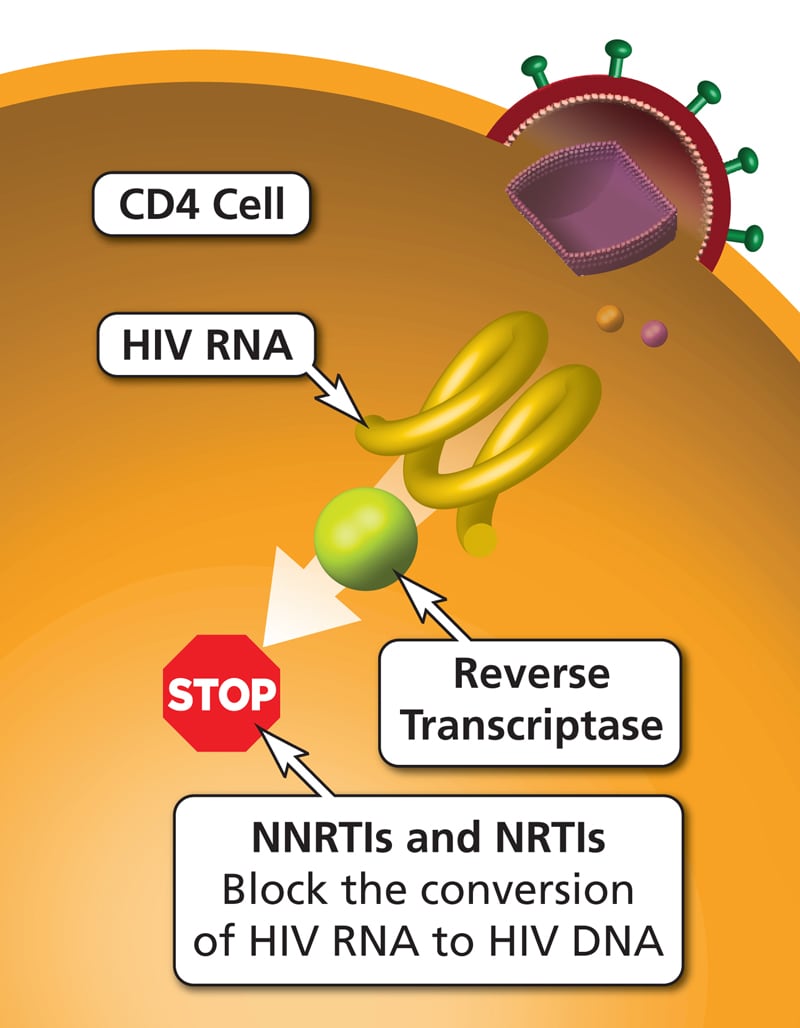

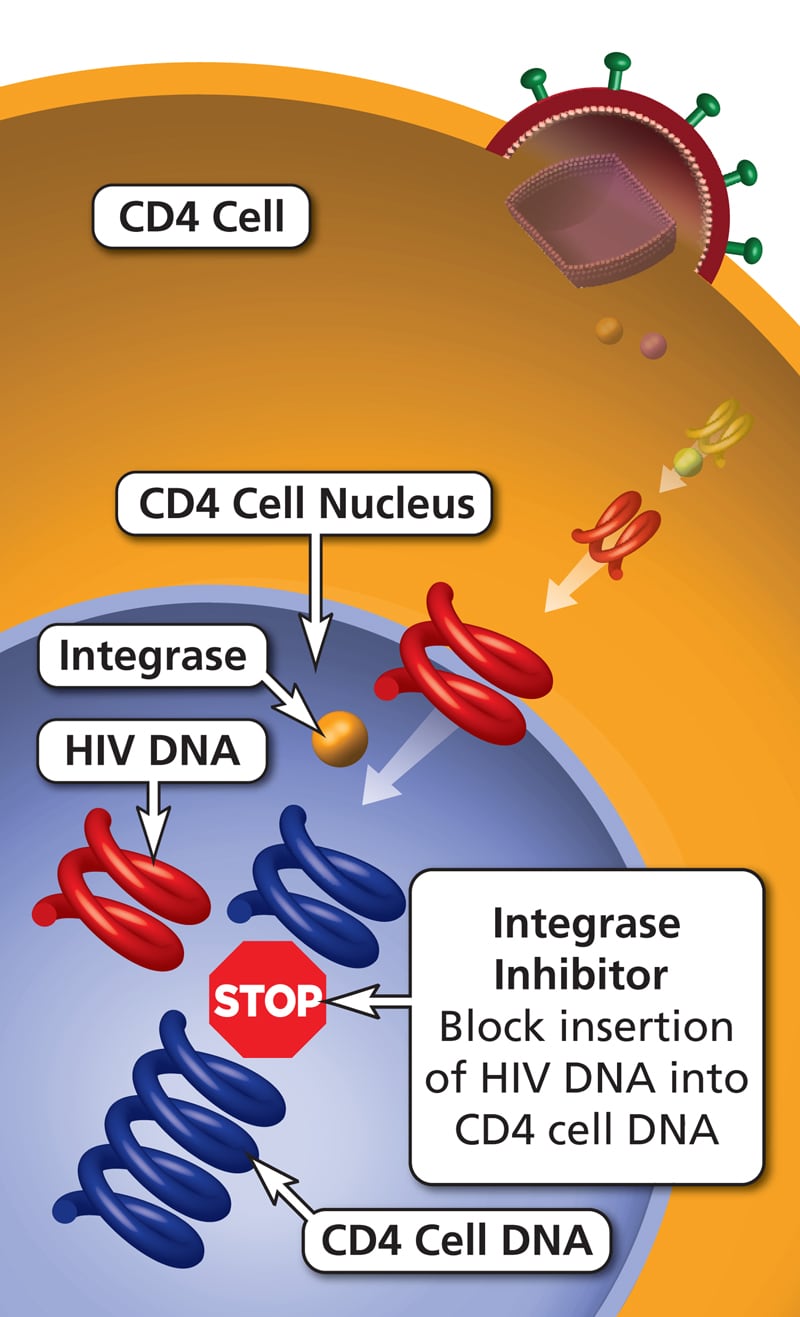
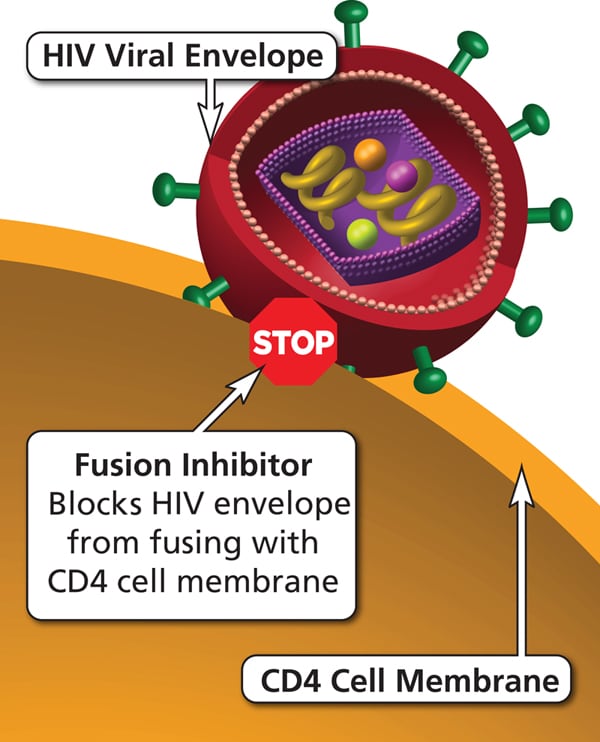
HAART regimens typically include a combination of two NRTIs plus one NNRTI, integrase inhibitor, or PI.
In pregnant patients, HAART regimens are composed of two NRTIs plus a PI or integrase inhibitor to prevent vertical transmission and transmission through breast milk.
Intrapartum zidovudine is given when viral loads are high (>1000 copies/ml) at 38 weeks, and it is also administered to the newborn as prophylaxis.
Lipid profile and blood glucose should be monitored before and after initiation of HAART.
Therapy should begin as soon as HIV positivity is detected.
Maintaining a plasma HIV RNA viral load of <200 copies/mL (including any measurable value below this threshold) with ART prevents sexual transmission of HIV to sexual partners.
Delavirdine, didanosine, indinavir, nelfinavir, and stavudine are no longer used due to the availability of better drugs, lower potency, and a higher incidence of adverse effects.

Sign up for free to take 1 quiz question on this topic