| Drug/ class | Mechanism of action | Characteristics and adverse effects |
| Tyrosine kinase inhibitors | ||
| Dasatinib, imatinib, nilotinib, erlotinib, sorafenib, sunitinib, crizotinib | Inhibit enzyme tyrosine kinase (TK) by competing with ATP for the binding site on TK. TKs are enzymes that cause ATP-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation and affect cell proliferation and signaling pathways. TKs include EGFR, PDGFR, VEGF and insulin receptors, Src kinases, Abl kinases, etc. Overexpression of TKs is seen in cancers. | High selectivity, efficacy, and fewer side effects. Used in CML, NSCLC, and renal cell cancers. Adverse effects include diarrhea, myalgia, CCF, and edema. Imatinib, nilotinib, and dasatinib inhibit Abl and PDGFR and inhibit bcr-abl expression; they are useful in CML and GIST. Erlotinib inhibits EGFR-related TKs. Sorafenib inhibits VEGF-related TKs. Sunitinib inhibits VEGF and PDGFR TKs. Crizotinib inhibits insulin receptor-related TKs. |
| Interferon alpha | Stimulates T cells to attack cancer cells. | Used to treat NHL, hairy cell leukemia, CML, renal cell cancers, melanoma, neuroendocrine tumors, and Kaposi’s sarcoma. Adverse effects include immunosuppression causing infections, decreased WBC count, diarrhea, insomnia, mood changes, headache, blurred vision, flu-like symptoms, alopecia, and rash. |
| Gonadal hormone antagonists | Tamoxifen: SERM (selective estrogen receptor modulator) with estrogen antagonist action on breast, and agonist action on endometrium and bone. Toremifene: derivative of tamoxifen, SERM. Raloxifene: SERM; estrogen antagonist on breast and endometrium, agonist on bone. Fulvestrant: SERD (selective estrogen receptor downregulator), anti-estrogen with no agonist activity; high-affinity competitive antagonist at ER alpha receptors. Flutamide: androgen receptor competitive antagonist. | Tamoxifen: used in ER+ breast cancer to prevent recurrence after chemotherapy. May cause pulmonary embolism, stroke, endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma, nausea, vomiting, and hot flashes. Toremifene: same as tamoxifen. Raloxifene: increased risk of venous thromboembolism, hot flashes, and leg cramps; used similarly to other SERMs and does not cause endometrial hyperplasia or cancer. Fulvestrant: used in ER+ breast cancer. Flutamide: used in metastatic prostate carcinoma; adverse effects include hot flashes, gynecomastia, decreased libido, impotence, cholestasis, and hepatic failure from inhibition of mitochondrial electron transport. |
| GnRH analogues | With constant dosing, both GnRH agonists and antagonists ultimately act antagonistically at GnRH signaling and decrease FSH and LH in the long run. Agonists may cause an initial, temporary rise in FSH and LH. Agonists include goserelin, histrelin, leuprolide, and triptorelin. Antagonists include degarelix. | Used in the treatment of prostate cancer. Adverse effects include hot flashes, gynaecomastia, decreased libido, fatigue, weight gain, edema, impotence, osteoporosis, glucose intolerance, and (rarely) hepatic failure. |
| Aromatase inhibitors | Inhibit the enzyme aromatase, which catalyzes the rate-limiting step in estrogen synthesis. | Anastrozole; letrozole (more potent than anastrozole); exemestane (steroidal); aminoglutethimide (not used now, non-selective). Used in advanced breast cancer. Adverse effects include hot flashes, nausea, diarrhea, edema, dyspnea, vaginal dryness, osteoporosis, increased cholesterol, and muscle and joint pains. |
| Asparaginase | A bacteria-derived enzyme that hydrolyzes L-asparagine to L-aspartic acid and ammonia in leukemic cells. This depletes asparagine, inhibits protein synthesis, causes cell-cycle arrest in the G1 phase, and triggers apoptosis in susceptible leukemic cell populations. | Used in the treatment of leukemias such as ALL and lymphomas. Adverse effects include hypersensitivity, bleeding, DVT, PE, leukopenia, acute pancreatitis, diarrhea, rash, and flu-like symptoms. |
| Proteasome inhibitors | Inhibit the catalytic activity of proteasomes, leading to inhibition of NFkB activity; altered degradation of cell-cycle proteins and apoptotic proteins; endoplasmic reticulum stress; inhibition of angiogenesis; and inhibition of DNA repair. This results in apoptosis of cancerous cells. | Used in leukemias, lymphomas, multiple myeloma, and solid organ tumors (except bortezomib). Bortezomib: causes peripheral neuropathy. Carfilzomib: fewer adverse effects. |
| Histone deacetylase inhibitors | Histone deacetylases (HDAC) inhibit gene transcription and regulate the activity of transcription factors and signaling molecules. HDAC inhibitors increase acetylation and therefore increase the stability of critical tumor suppressors and transcription factors such as p53 and RUNX3. | Vorinostat; romidepsin/depsipeptide; apicidin. Adverse effects include diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, PE, thrombocytopenia, and granulocytopenia. |
| Monoclonal antibodies | ||
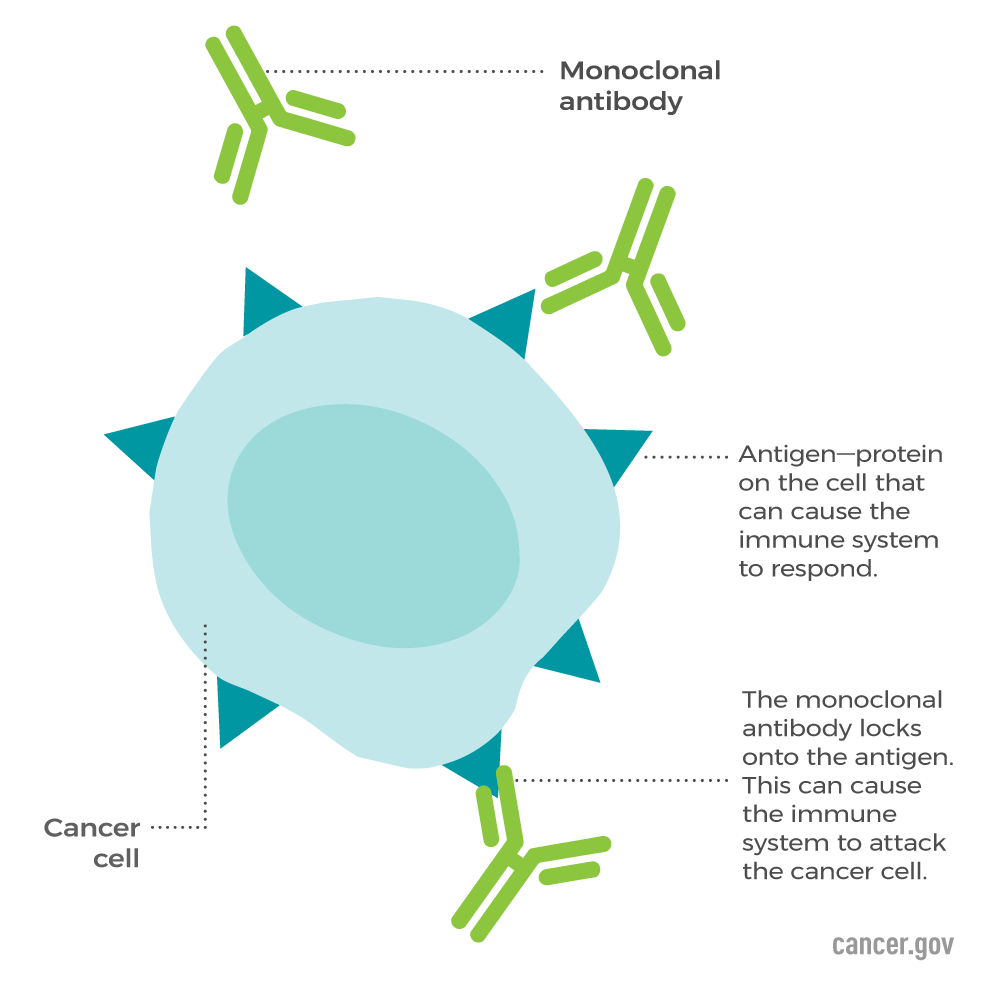
| Rituximab | Monoclonal antibody to CD 20 on B cells; targets the cancerous cell so it can be killed by the immune system. | Adverse effects of monoclonal antibodies include needle-site reactions, flu-like symptoms, pain, swelling, rash, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, CCF, HT, AMI, mouth ulcers, ILD, capillary leak syndrome causing shock and organ failure, and cytokine storm. Trastuzumab is used in the treatment of HER 2 positive breast cancer and gastric cancers. |
| Blinatumomab | Monoclonal antibody to CD 19 on leukemic B cells and CD3 on T cells; helps T cells kill the leukemic B cells. | |
| Trastuzumab/Herceptin, humanized IgG1 | Monoclonal antibody to HER2 (ErbB2); causes ADCC and inhibits HER2 signaling. | |
| Bevacizumab, humanized IgG1 | Monoclonal antibody to VEGF. | |
| Cetuximab, chimeric human/murine IgG1 | Monoclonal antibody to EGFR (ErbB1). | |
| Immune checkpoint inhibitors | Immune checkpoint proteins such as PD1, PD L1, or CTLA4 on tumor cells bind to T cells and prevent tumor killing by T cells. Immune checkpoint inhibitors bind to checkpoint proteins (such as PD L1), allowing T cells to kill the tumor cells. | PD 1 inhibitors include pembrolizumab, nivolumab, and cemiplimab. PD L1 inhibitors include atezolizumab, avelumab, and durvalumab. CTLA4 inhibitors include ipilimumab (a monoclonal antibody). Adverse effects include rash, diarrhea, fatigue, itchiness, hepatitis, hypophysitis, myocarditis, nephritis, diabetes, pancreatitis, pneumonitis, muscle weakness, and dyspnea. |
| All-trans retinoic acid | Derivative of Vit A; induces differentiation, cell-cycle arrest, and apoptosis of leukemic cells. It forms complexes with nuclear receptors (RARs) that promote transcription. | Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Adverse effects include flu-like symptoms, headache, depression, dry skin and mucosa, nausea, vomiting, rash, mouth ulcers, vision changes, edema, arrhythmias, hyperleukocytosis, leukostasis with blood clots, cheilitis, and elevation of serum triglycerides and cholesterol. |
Sign up for free to take 3 quiz questions on this topic