It’s usually considered a nosocomial pathogen and is widely known for antibiotic resistance, including ESBLs (extended-spectrum beta-lactamases).
It’s mainly associated with:
You’ll most often see it in hospital settings or in immunodeficient individuals, such as older adults, people with chronic diabetes, and chronic alcohol use.
In pneumonia, a very characteristic “currant jelly” sputum is produced. Why does this happen? (Hint: it relates to a colony characteristic.)
Interestingly, two other species are found infrequently:
Diagnosis is typically done with Gram stain and culture of clinical samples.
On Gram stain:
On culture:
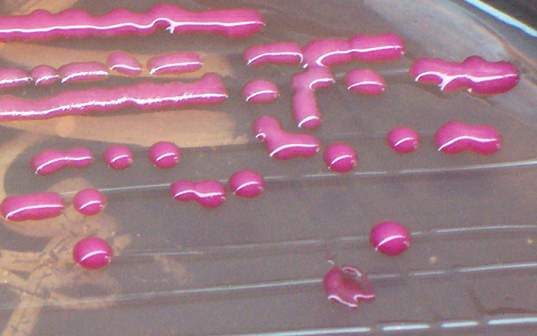
Sign up for free to take 1 quiz question on this topic