Histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine are essential amino acids because they can’t be synthesized in the human body.
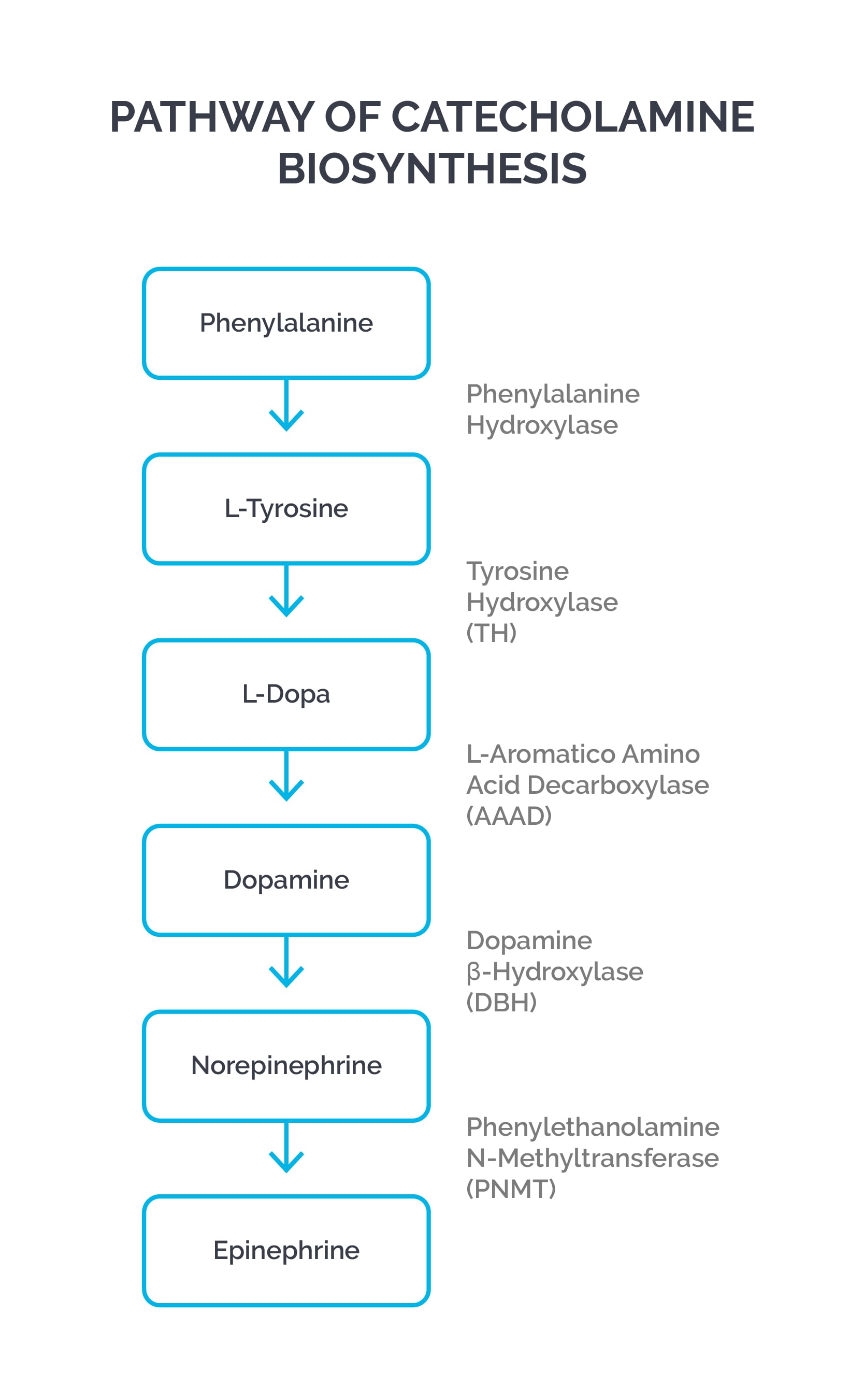
Tyrosine is synthesized from phenylalanine metabolism, and cysteine is synthesized from methionine metabolism. Tyrosine becomes an essential amino acid in PKU.
| Disease name | Enzyme deficient | Characteristics |
| Phenylketonuria (PKU) | Classic form: Phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) deficiency; Malignant PKU: dihydrobiopterin reductase deficiency, which is needed to convert dihydrobiopterin to tetrahydrobiopterin (a cofactor for PAH); deficiency of dopamine and serotonin | Mental retardation, seizures, albinism, eczema, “mousy” odor, vomiting; phenylketones are neurotoxic metabolites; untreated maternal PKU can cause mental retardation, IUGR, microcephaly, and heart defects in newborns; patients with malignant PKU can have neurological deficits even after phenylalanine restriction; treat with dietary restriction of phenylalanine and tyrosine supplementation; sapropterin supplementation; pegvaliase to lyse phenylalanine |
| Maple syrup urine disease | Branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase deficiency; affects the breakdown of isoleucine, leucine, and valine | Poor feeding/irritability, progressing to lethargy, intermittent apnea, cerebral edema, coma, and death; “maple syrup” odor (from accumulation of 2-hydroxyisoleucine); elevations of valine, leucine, and isoleucine, as well as L-alloisoleucine and the respective ketoacids; treatment is protein restriction to minimum requirements and hemodialysis for acute crisis |
| Alkaptonuria | Homogentisate oxidase deficiency | Homogentisic acid accumulates, causing pigmentation of connective tissue (e.g., sclera of the eye or ear cartilage), arthritis of joints and spine, cardiac valve involvement, and kidney and prostate stones; urine turns dark/black when exposed to air; treatment is nitisinone, restriction of tyrosine and phenylalanine, high-dose vitamin C, and oral bisphosphonate |
| Homocystinuria (homocysteinemia) | Cystathionine synthase deficiency; pyridoxine (vitamin B6) deficiency | Homocysteine causes endothelial damage with thrombosis; presents with myopia, dislocated lens, osteoporosis, developmental delay, learning disabilities, marfanoid features, and megaloblastic anemia in some cases; elevated levels of homocysteine and methionine; treatment is high doses of vitamin B6, restriction of methionine, and cysteine supplementation |
| Albinism | Tyrosinase deficiency | Absence of melanin pigment in melanocytes; colorless hair and skin; lack of pigment in the eye causing photophobia; increased risk of skin cancer; no neurological deficits (compare and contrast with PKU) |
| Tyrosinemia* | Type I (tyrosinosis): fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (FAH) deficiency; Type II: tyrosine aminotransferase (TAT) deficiency; Type III: 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPD) deficiency; all three types decrease the breakdown of tyrosine | Type I is most severe, beginning in infancy with failure to thrive, diarrhea, vomiting, jaundice, cabbage-like odor, recurrent nosebleeds, liver and kidney failure, rickets, hepatocellular carcinoma, and peripheral neuropathy; Type II presents in early childhood with eye pain and redness, excessive tearing, photophobia, thick painful skin on the palms and soles (palmoplantar hyperkeratosis), and intellectual disabilities; Type III presents with intellectual disability, seizures, and intermittent ataxia; diagnosis is by elevated levels of tyrosine and metabolites (e.g., phenyl lactates, phenyl pyruvates, etc.); treatment is a tyrosine-restricted, low-protein diet and nitisinone |
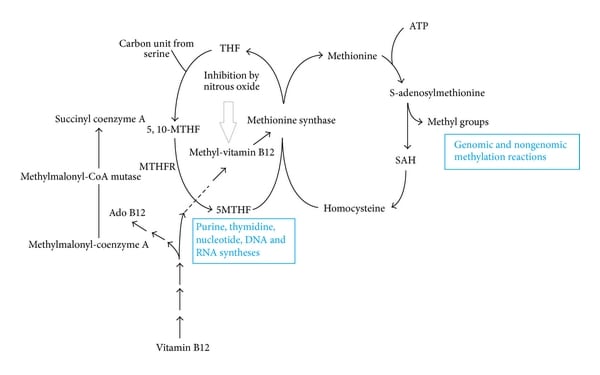
Pathways of intracellular vitamin B12 metabolism. MTHFR: methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase; 5,10-MTHF: 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate; 5-MTHF: 5-methylenetetrahydrofolate; THF: tetrahydrofolate; SAH: S-adenosyl homocysteine.
Sign up for free to take 1 quiz question on this topic