Both T and B lymphocytes originate from a common lymphoid progenitor in the bone marrow. After that, they develop in different places:
Development of T cells: T cells can be divided into two lineages based on their surface receptors:
Alpha, beta T cells are further divided into CD4 and CD8 T cells based on which class of MHC they recognize:
Early in development, T cells do not express either CD4 or CD8. These are called “double negative” T cells. Later, thymocytes may express both CD4 and CD8; these are called “double positive” T cells, and they are precursors to CD4 and CD8 T cells.
Location in the thymus changes as T cells mature:
Surface markers also change with maturation:
The hormones thymosin and thymopoietin help T cell differentiation in the thymus.
During thymic development, T cells are tested for how they respond to self MHC and self antigens:
A transcriptional regulator called AIRE (Autoimmune Regulator) enhances the synthesis of an array of self-proteins to be displayed on thymic epithelial cells, which helps establish T cell tolerance. Mutations in AIRE cause Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy.
Different thymic cells support these selection steps:
Mature, single positive CD4 or CD8 T cells then leave the thymus:
The CD4 molecule is composed of four domains: D1,2,3 and 4. Domains D1 and D2 are involved in binding to the MHC class II molecule.
A CD8 molecule is a heterodimer of one alpha and one beta chain or two alpha chains that are linked to each other. CD8 binds to the alpha 3 domain on MHC I.
CD4 and CD8 act as co-receptors and bind to MHC II or I, respectively. This binding is essential for an effective immune response.
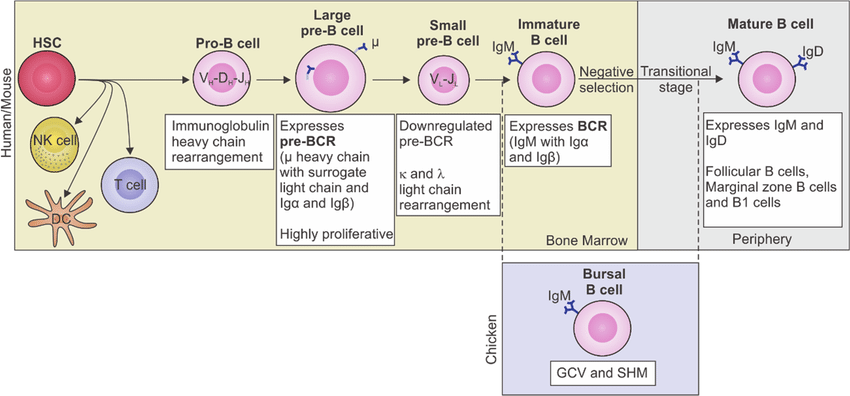
Development of B cells: Bone marrow stromal cells are essential in the early stages of B cell development. Stromal cells secrete several growth factors like stem cell factor, cytokines and adhesion molecules to help B cell differentiation.
As B cells mature, their surface immunoglobulins change:
B cell surface proteins CD45R and CD19 are expressed in all stages of B cell development. Self-reactive B cells undergo clonal deletion.
Sign up for free to take 2 quiz questions on this topic