Blood transfusions are the most common type of transplant.
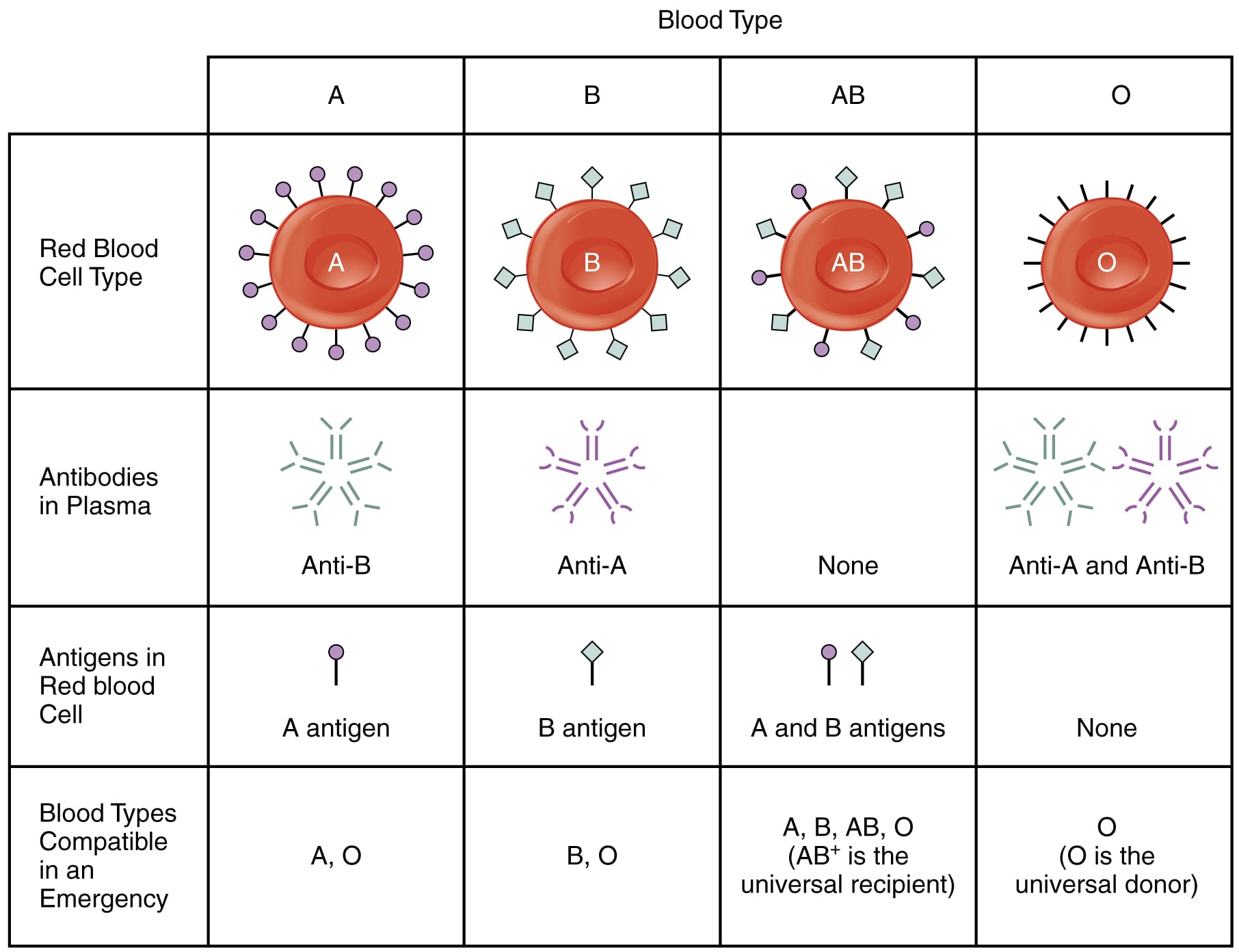
| Type of reaction | Features |
| Febrile reactions | Fever and chills due to cytokine release from donor WBCs; caused by host antibodies reacting against antigens on donor WBCs |
| Allergic reactions including anaphylaxis | Hives and itching; rarely anaphylaxis (especially in patients with selective IgA deficiency); caused by antibodies to plasma proteins or other antigens in the donor blood |
| Hemolytic reactions | DIC, renal failure, back or flank pain, bloody urine, hemoglobinuria, hypotension; can be fatal; due to ABO or other blood group antigen mismatch; caused by host antibodies to antigens on donor RBCs |
| Alloimmunization | After a previous pregnancy or a prior blood/blood product transfusion, patients may develop alloantibodies to RBCs; during a subsequent transfusion, these alloantibodies may cause a hemolytic transfusion reaction |
| Transfusion related acute lung injury | Typically seen in patients with pneumonia, recent surgery, or other pulmonary illness; donor antibodies to HLA or leukocyte antigens react against host WBCs and tissues, causing inflammation and acute pulmonary edema |
GVHD can occur after a blood transfusion. Massive transfusion may cause hypothermia, acidosis, coagulopathy, and citrate toxicity. Electrolyte imbalances such as hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, hypokalemia, or hyperkalemia may occur.
Sign up for free to take 1 quiz question on this topic