Drugs used in the treatment of gout: Some drugs are used to treat acute gout flares, while others are used to prevent frequent attacks.
NSAIDs, steroids, and colchicine are used to treat gout flares. NSAIDs like ibuprofen or indomethacin may need to be used in high doses to treat gout flares. Colchicine is preferably administered within 12-24 hours of flare onset. Oral prednisone or intra-articular steroids are used to decrease inflammation during a flare. IL-1 receptor antagonist anakinra and the anti-IL-1 antibody canakinumab are newer drugs that can be used in acute flares when other drugs are not effective.
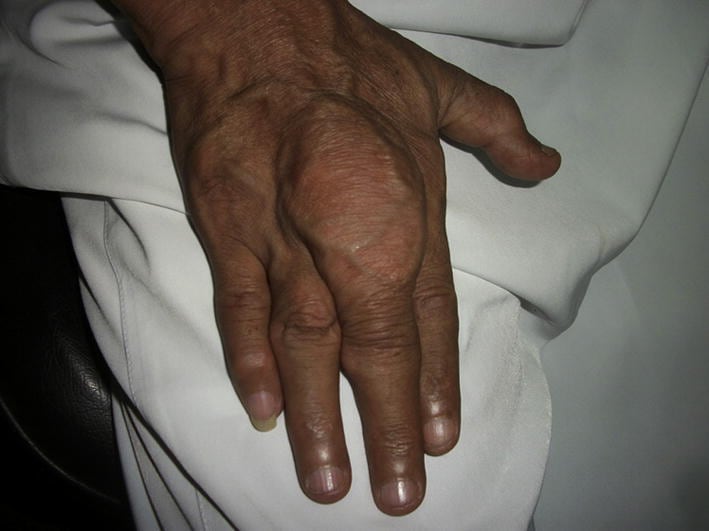
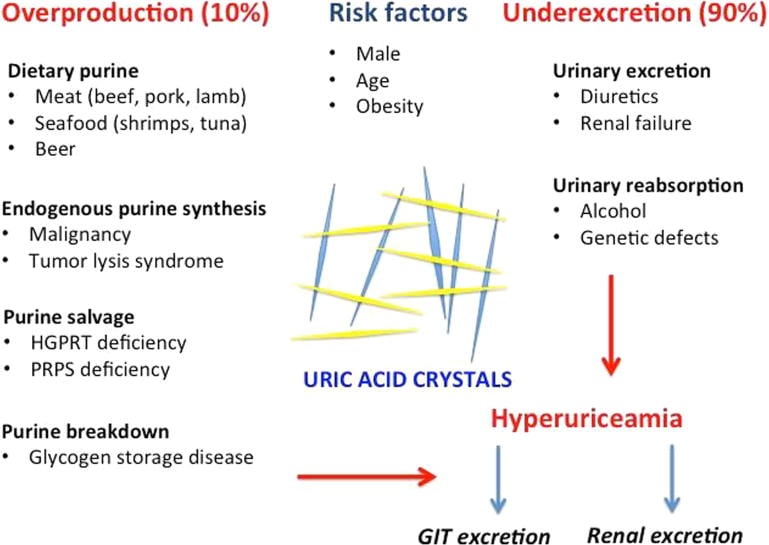
Uric acid-lowering drugs are used to prevent flares and long-term complications. When initiating these drugs, there may be a temporary rise in the frequency of flares. The following drugs are used:
Allopurinol: Decreases uric acid levels by inhibiting the enzyme xanthine oxidase. Adverse effects include nausea, diarrhea, elevated liver enzymes, myelosuppression, acute interstitial nephritis, hypersensitivity, SJS, TEN, rashes, gynecomastia, and peripheral neuropathy. Allopurinol should not be used with azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine because their metabolism is dependent on xanthine oxidase.
Febuxostat: A non-purine xanthine oxidase inhibitor. It has a better safety profile than allopurinol and can be prescribed in renal failure as well. Adverse effects include skin rashes, hepatotoxicity, and nephrotoxicity. It should be used cautiously in patients with cardiovascular diseases.
Uricosuric drugs: Lower uric acid levels by increasing the secretion of uric acid in the urine. Initially, they may precipitate uric acid stones. They include probenecid, sulfinpyrazone, benzbromarone, and lesinurad (inhibits URAT1 and OAT4, or organic anion transporters).
Rasburicase: A recombinant urate oxidase enzyme that converts uric acid to allantoin, which can be easily excreted in the urine. Rasburicase is primarily used to treat tumor lysis syndrome because it decreases uric acid levels acutely. It can be used to manage tophaceous gout. Adverse effects include anaphylaxis, methemoglobinemia, and infusion site reactions. It is contraindicated in G6PD deficiency because hydrogen peroxide is a product of rasburicase.
Lifestyle modification includes weight loss in obese patients and avoiding alcoholic beverages, meat, a high-protein diet, and sugary drinks. Thiazides and loop diuretics increase uric acid levels and should be stopped or substituted if possible.
NSAIDS or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Prostaglandins are formed from arachidonic acid by the action of cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2) enzymes.
NSAIDs block COX enzymes, reducing the formation of inflammatory prostaglandins (as well as prostanoids and thromboxanes).
Aspirin exerts its effects by non-competitive and irreversible inhibition of COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, blocking the conversion of arachidonic acid into PGH2. In platelets, TXA2 production is entirely COX-1 dependent. Irreversible COX-1 binding by aspirin permanently prevents TXA2 production and subsequently inhibits platelet aggregation for the duration of the platelet life cycle (about 7-10 days).
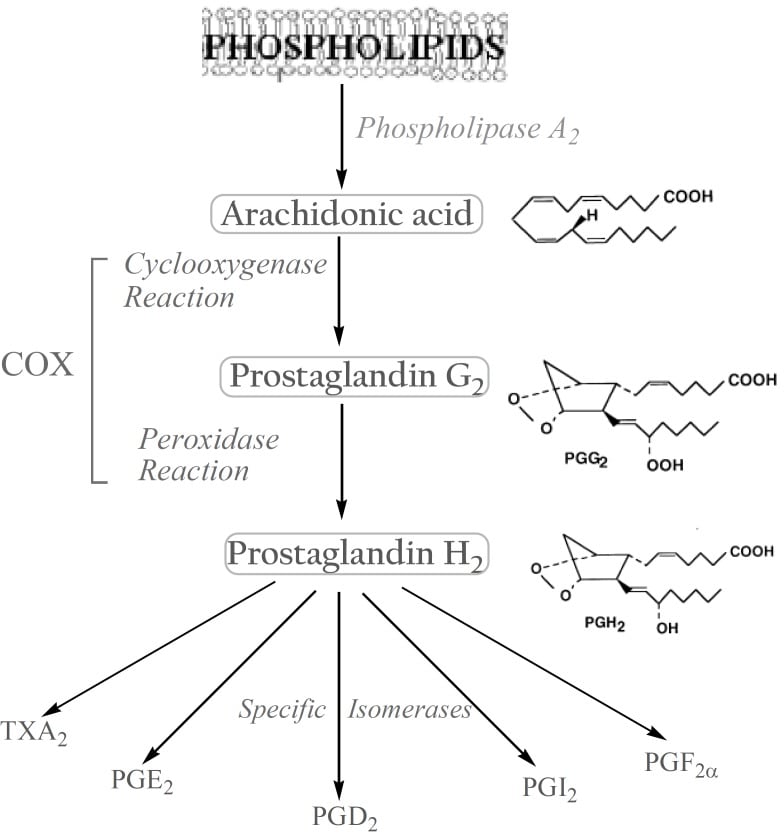
NSAIDs like ibuprofen, diclofenac, ketorolac, indomethacin, and naproxen are non-selective, reversible inhibitors of COX-1 and COX-2. Celecoxib, rofecoxib, and valdecoxib are selective COX-2 inhibitors. Paracetamol inhibits the PGH2 synthase enzyme. It has antipyretic and analgesic effects by a central mechanism, but it is not anti-inflammatory.
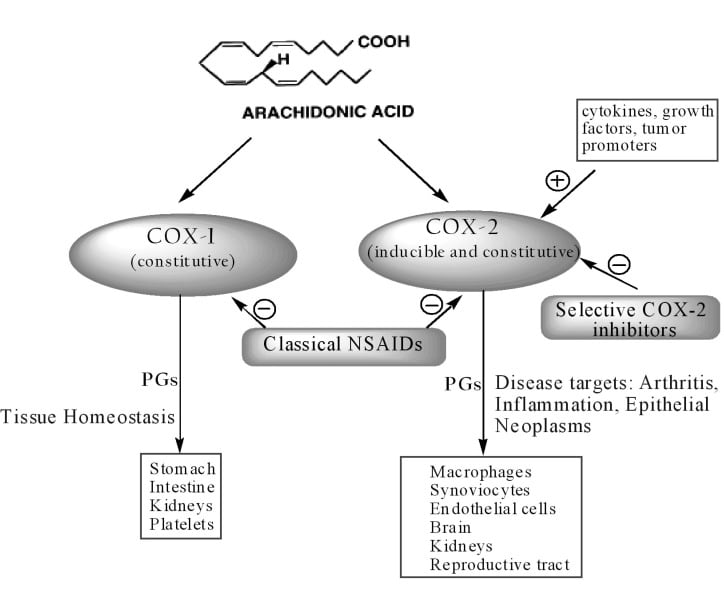
Adverse effects include dyspepsia, peptic ulcers, GI bleeding and perforation, sodium retention, edema, renal failure, renal papillary necrosis, stroke, AMI, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease. Diclofenac and COX-2 selective blockers like celecoxib are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events and stroke (due to an indirect increase in COX-1-mediated thromboxane synthesis).
NSAID-induced gastroduodenal ulcers can be prevented by GI protective agents such as misoprostol, H2-receptor antagonists, or proton pump inhibitors. COX-2 inhibitors cause less GI ulceration compared with non-selective NSAIDs.
Children treated with aspirin during a viral infection may develop Reye’s syndrome with fulminant hepatic necrosis and failure. Aspirin overdose causes respiratory alkalosis initially, followed by metabolic acidosis from mitochondrial toxicity. Toxicity of paracetamol is mainly related to the liver.
Drugs used in the prevention and/or treatment of osteoporosis: These can be divided into two broad groups: antiresorptive and anabolic.
Antiresorptive medications slow down the breakdown (resorption) of bone by osteoclasts. This helps prevent bone loss and lowers the risk of fracture. They include the drugs below:
Anabolic medications help to form new bone, increase bone density, and can also reduce the risk of fractures. Teriparatide is the only drug in this class.
Teriparatide: An injectable recombinant human PTH. Like PTH, it acts directly on osteoblasts and cells of the osteoblast lineage. It promotes differentiation of pre-osteoblasts to osteoblasts and inhibits osteoblast apoptosis. It also triggers the production of several growth factors in bone, such as insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I). Adverse effects include nausea and headache. It may increase the risk of osteosarcoma.
Sign up for free to take 3 quiz questions on this topic