What is spread?
Spread (also called variation or dispersion) describes how data values are distributed around a central value.
Measures of spread include the following:
Steps to calculate the SD:
Step 1. Calculate the arithmetic mean.
Step 2. Subtract the mean from each observation.
Step 3. Square each difference.
Step 4. Sum the squared differences.
Step 5. Divide the sum of the squared differences by n − 1.
Step 6. Take the square root of the value obtained in Step 5. The result is the standard deviation.
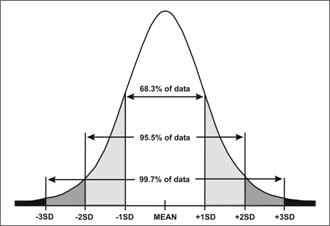
Bell-shaped curve with the standard deviations equally distributed on the x-axis. 99.7% of the data falls between the minus 3 and plus 3 standard deviation. 95.5% of the data falls between the minus 2 and plus 2 standard deviation. 68.3% of the data falls between the minus 1 and plus 1 standard deviations.
Standard error of mean (SEM): The SEM measures how far the sample mean is likely to be from the true population mean. The SEM is always smaller than the SD.
SEM = Standard deviation/ square root of n, where “n” is the number of observations.
SEM is used to calculate confidence intervals around the arithmetic mean.
Confidence intervals or confidence limits (CI): A confidence interval is a range of values that is likely to contain a population parameter (such as the mean). It is expressed as a percentage (e.g., 95%, 99%).
CI is given by the formula,
CI = Mean + or - Z x SEM
A CI is reported as a range with a lower and upper limit. For a 95% CI, Z = 1.96. For a 99% CI, Z = 2.58.
Problem 1: Find the 95% confidence interval for a mean total cholesterol level of 206, standard error of the mean of 3.
Using the formula above, upper limit = 206 + 1.96 X 3 = 211.88
Lower limit = 206 - 1.96 X 3 = 200.12
CI is 200.12 to 211.88.
In other words, the best estimate of the true population mean total cholesterol from the given data is 206, but the true mean could reasonably lie anywhere between 200.12 and 211.88.
If the CI of two groups does not overlap, then it means that a statistically significant difference exists. If the CI of two groups overlap, then it means that no significant difference exists.
Sign up for free to take 2 quiz questions on this topic