Lysosomal storage disorders
Lysosomal storage disorders
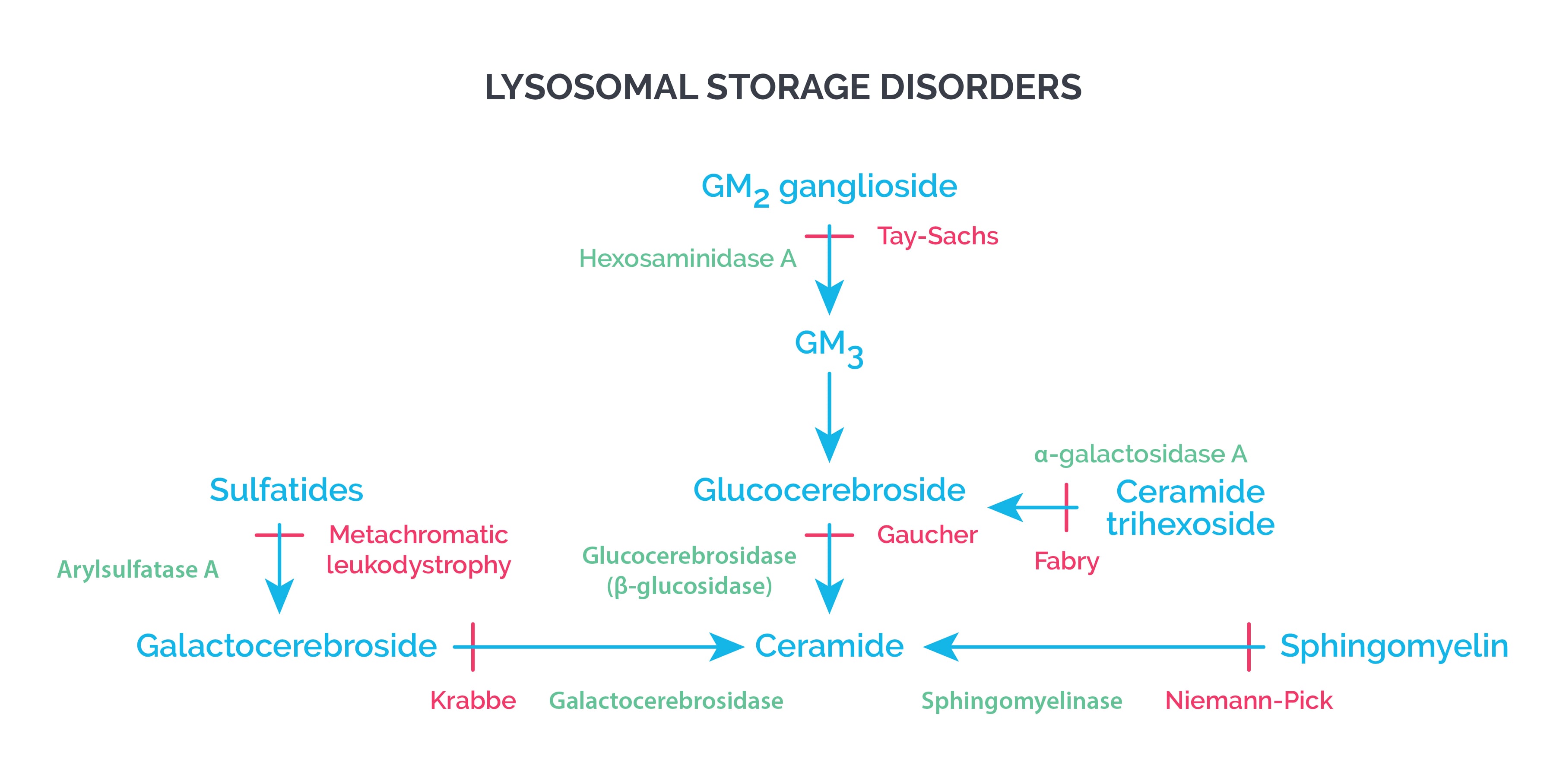
Lysosomal storage disorders are caused by deficiencies of specific lysosomal enzymes. When an enzyme is missing or not working, its substrate can’t be broken down, so it accumulates inside lysosomes.
Most lysosomal storage disorders are autosomal recessive (AR). The main exception is Fabry disease, which is X-linked.
The following types are seen:
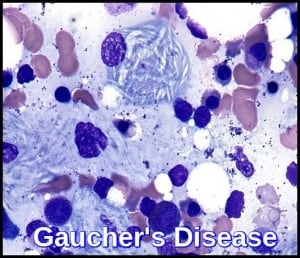
- Gaucher’s disease
- Accumulation of glucocerebrosides
- Most common LSD
- Hepatosplenomegaly, osteoporosis, rarely CNS involvement, pancytopenia
- Treat with enzyme replacement therapy
- “Crumpled tissue paper” cytoplasm of macrophages called Gaucher cells
- Tay Sachs disease
- Accumulation of GM2 gangliosides
- Rapid, progressive, fatal neurodegeneration
- Blindness
- Muscular weakness, seizures
- Cherry red spot on the macula
- Onion skinning of lysosomes
- No hepatosplenomegaly
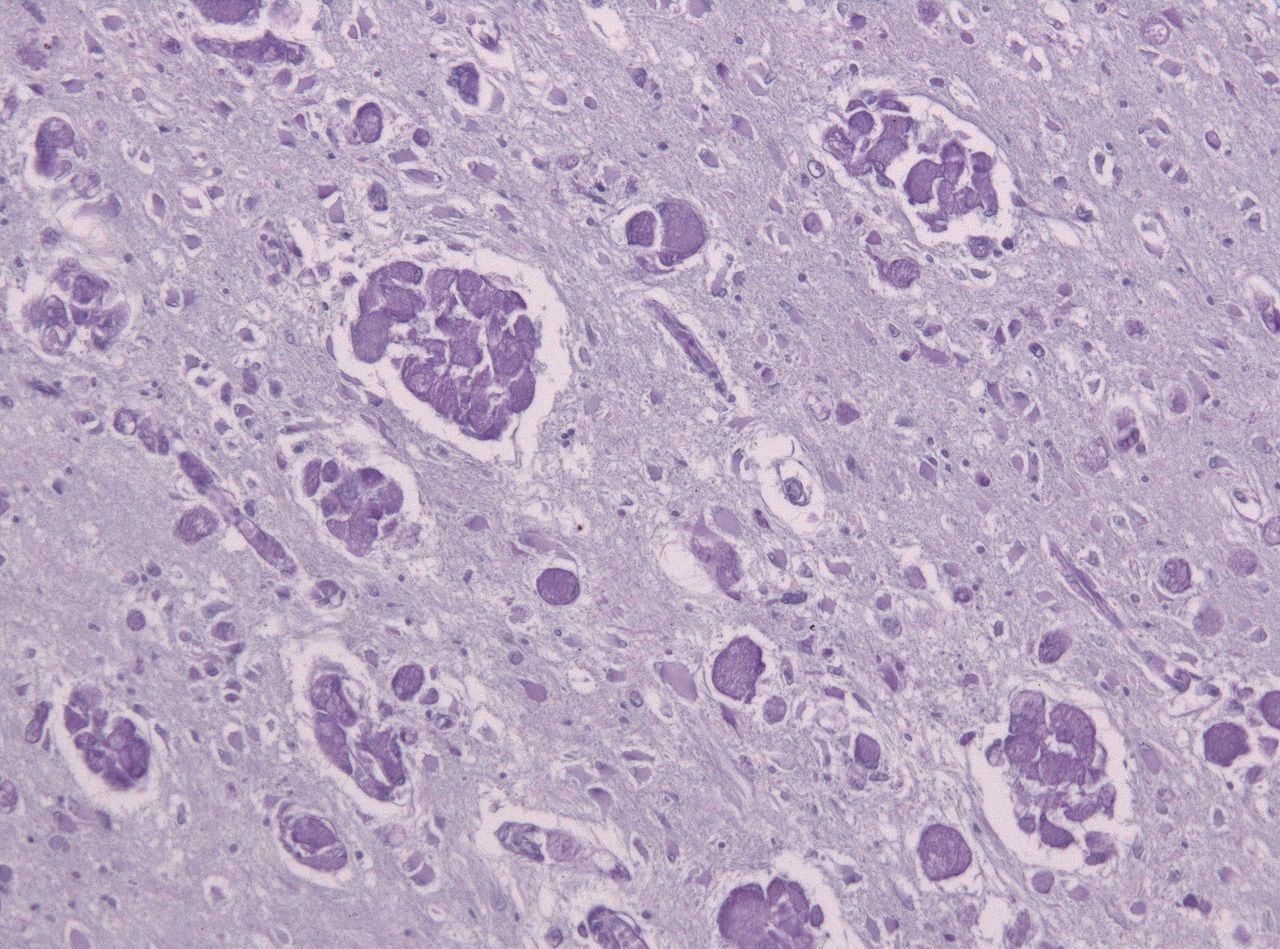
- Krabbe disease (Globoid cell leukodystrophy)
- Accumulation of galactocerebrosides
- Mental and motor retardation
- Blindness, deafness, loss of myelin
- Globoid bodies (glycolipid laden macrophages) seen in the white matter of the brain
- Metachromatic leukodystrophy
- Accumulation of sulfatides
- Demyelination, cognitive deterioration, ataxia
- Progressive paralysis, infantile dementia
- Nerves stain yellow-brown with crystal violet
- Niemann-Pick disease
- Accumulation of sphingomyelin
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Type A shows neurodegeneration
- Cherry red macula, lipid laden foam cells
- Fabry’s disease
- Accumulation of globosides
- Only X linked LSD.
- Red-purple skin rash, angiokeratomas
- Renal and heart failure
- Burning pain in lower extremities