These fungi aren’t confined to the skin; they can cause systemic infections. The clinical spectrum ranges from asymptomatic infection to life-threatening disease. Some cause opportunistic infections in immunocompromised individuals.
It’s a dimorphic fungus endemic to the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys. Infection is transmitted by inhalation of spores. The organism is found in soil contaminated with bird droppings and in bat-infested caves.
Most infections are asymptomatic. When symptomatic, it can present with fever and pneumonia-like symptoms. It may also cause skin ulcers and granulomas. In particular, watch for palatal ulcers or disseminated disease in AIDS patients, which can present with hepatosplenomegaly and lymphadenopathy.
For laboratory diagnosis:
This is also a dimorphic fungus endemic to the Great Lakes area and the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys. Infection occurs by inhalation of spores.
Clinically, it presents with pneumonia-like symptoms, fever, and chest pain. Disseminated disease can cause abscess formation, osteomyelitis, and other systemic findings. It may also cause skin nodules, ulcers, and fistulas after local inoculation due to trauma.
The most reliable way to differentiate it from histoplasmosis is microscopy, which shows thick-walled yeast with “broad-based” budding.
Laboratory findings:
It’s endemic in the southwestern USA (California, southern Nevada, Arizona, etc.). Coccidioidomycosis is also called Desert Valley fever, Desert Rheumatism, or San Joaquin Valley Fever.
Infection is caused by inhalation of arthrospores. Clinically, it presents with fever, chronic cough that can mimic tuberculosis, myalgia, arthralgias, and erythema nodosum. In immunocompromised individuals, it may disseminate and cause meningitis, osteomyelitis, lymphadenopathy, and other systemic disease.
Diagnosis is primarily by tissue biopsy, which shows characteristic thick-walled spherules containing endospores.
Additional laboratory features:
It’s a dimorphic fungus endemic to South America. Infection is acquired by inhalation of spores.
It can present with fever, cough, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, oral and buccal ulcers, and hepatomegaly. The adrenal glands may be involved in disseminated disease.
Laboratory diagnosis:
Cryptococcus neoformans is the most pathogenic Cryptococcus species in humans. Cryptococcus gattii is also seen in some cases.
Exposure to pigeon droppings and old buildings increases the risk of infection via inhalation. Infections occur in both immunocompetent and immunodeficient individuals. It’s an AIDS-defining illness for 60-70% of HIV-infected patients.
Clinical presentations include:
Diagnosis:
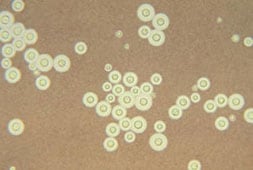
A photomicrograph of C. neoformans stained with India ink.
Candida are commensal organisms in the upper respiratory, gastrointestinal, and female genital tracts. They can cause skin and subcutaneous tissue infections, as well as intravenous catheter-associated infections.
Risk factors include diabetes mellitus, antibiotic therapy, moist skin folds, obesity, and immunodeficiencies. The source of infection is often endogenous. Candida albicans is the most commonly implicated species.
Clinical features: It has varied manifestations. Common presentations include oral thrush (white patches in the oral cavity); vulvovaginitis (curd-like white discharge with itching and burning); intertrigo (inflamed lesions of skin folds); diaper rash (especially if diapers aren’t changed frequently); esophagitis; paronychia (infection of the nail fold); onychomycosis; and systemic infections such as endocarditis, UTI, pneumonia, meningitis, arthritis, and endophthalmitis. Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis is a condition in which lesions are limited to the skin and mucosa and results from deficient cell-mediated immunity.
Laboratory diagnosis of Candidiasis: Diagnosis is made by demonstrating budding yeast cells and pseudohyphae in samples such as sputum, CSF, swabs, and biopsy specimens. They are Gram positive. The presence of pseudohyphae indicates tissue invasion and active infection. Culture shows creamy colonies. The germ tube test is positive in C. albicans. ELISA, latex agglutination, immunoblot, and CIEP can be used for antibody detection. PCR and DNA probes can help diagnose systemic infections.
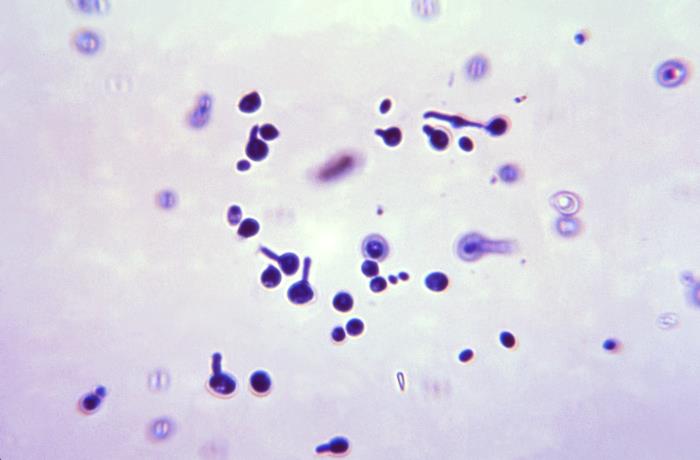
Stained using the Gram-stain technique, this photomicrograph revealed these Candida albicans fungal spores, that had been suspended in an animal serum specimen, and allowed to grow, giving rise to filamentous germ tubes.
Sign up for free to take 2 quiz questions on this topic