They are aerobic, slow-growing, filamentous or rod-shaped, acid-fast bacilli. Their acid-fastness is due to a waxy, lipid-rich layer of mycolic acid in the cell wall. They don’t take up the Gram stain. Cord factor is a glycolipid in the cell wall and is associated with virulence. M. tuberculosis is the organism responsible for tuberculosis (TB).
TB is acquired by inhalation. M. tuberculosis is then ingested by alveolar macrophages, where it survives within the phagosome by inhibiting phagosome-lysosome fusion. The primary lesion is typically seen in the lower lobes of the lung; together with enlarged draining lymph nodes, this forms the Ghon’s complex. Reactivation lesions occur in the apical lobes of the lung. TB causes caseous granulomatous inflammation, forming tuberculomas.
Clinically, TB presents with fever, night sweats, chronic cough with expectoration, hemoptysis, weight loss, and loss of appetite. Pleural effusions may occur. M. tuberculosis or M. bovis may cause gastrointestinal tuberculosis, presenting as abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and fever. Other organs (kidneys, bones, meninges, etc.) may also be involved. A disseminated form of tuberculosis with multiple small tubercles in internal organs is seen in miliary tuberculosis.
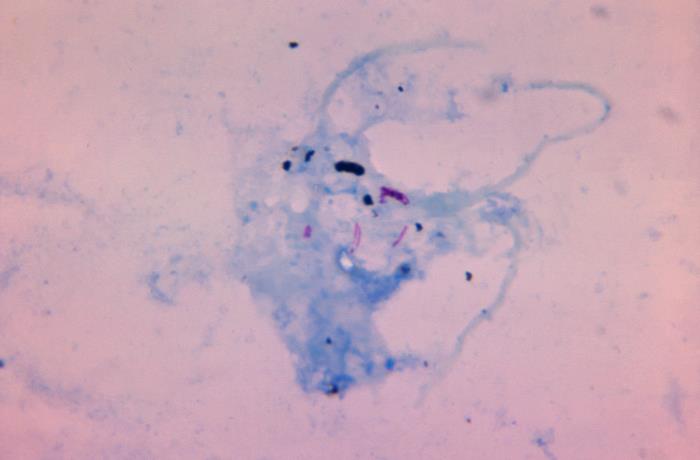
This photomicrograph of a Ziehl-Neelsen-stained specimen, revealed the presence of magenta stained, rod-shaped, acid-fast, Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacilli.
Laboratory diagnosis is done by acid-fast staining of sputum or gastric lavage fluid. Auramine staining (showing yellow rods) can be used for rapid diagnosis. Special media such as Lowenstein-Jensen agar is used, and growth may take up to 8 weeks.
BACTEC is a special radiometric liquid medium containing radiolabeled C14. Detection of CO2 14 indicates bacterial growth. M. tuberculosis can be confirmed by biochemical tests: niacin positive, weakly catalase positive, nitrate reduction positive, sensitivity to pyrazinamide, and resistance to TCH.
Ribosomal RNA or DNA can be detected in tissue samples by nucleic acid amplification tests such as PCR, ligase chain reaction, strand displacement amplification, DNA probes, and microarray methods. Antibody detection can be done by ELISA, radioimmunoassay, or latex agglutination tests.
For diagnosis of latent infection, the tuberculin/PPD skin test, gamma interferon release assay, or Quantiferon Gold assay is used.
MODS (“microscopic observation drug susceptibility”) assay is a technique for rapid detection of M. tuberculosis and drug-resistant TB. It uses a liquid culture medium to which INH or rifampin can be added to test for resistance. Growth is observed microscopically by sampling the liquid medium rather than waiting for colonies to appear.
They are present in the environment and can be differentiated from M. tuberculosis by being niacin negative, aryl sulfatase positive, resistant to antituberculosis drugs, with some being rapid growers and some producing pigment.
| Microorganism | Disease Caused |
| M.kansasii | TB like lung disease |
| M.marinum | Swimming pool granuloma or fish tank granuloma, skin ulcers |
| M.scrofulaceum | Scrofula (cervical adenitis) |
| M.avium intracellulare | TB like lung disease in AIDS |
| M fortuitum and M chelonei | Skin, subcutaneous infections following puncture wounds |
Sign up for free to take 3 quiz questions on this topic