Translation is the process of converting the nucleotide sequence of an mRNA molecule into an amino acid sequence during protein synthesis. The ribosome reads the mRNA in groups of three bases (codons) to assemble a protein.
Translation has three stages as follows:
Initiation: Near the 5’ end of mRNA is a region called the untranslated region (UTR), also known as the leader sequence. This portion of mRNA lies between the first nucleotide that is transcribed and the start codon (AUG) of the coding region. The leader sequence is important because it contains a ribosome-binding site.
First, three initiation factor proteins (IF1, IF2, and IF3) bind to the small ribosomal subunit. This preinitiation complex, along with a methionine-carrying tRNA, then binds to the mRNA near the AUG start codon, forming the initiation complex on the mRNA.
The small ribosomal subunit has three binding sites:
The initiator tRNA carrying methionine binds to the AUG start codon at the ribosome’s P site. This methionine becomes the first amino acid incorporated into the growing polypeptide chain. Once the initiation complex is formed, the large ribosomal subunit binds, which causes the release of the initiation factors.
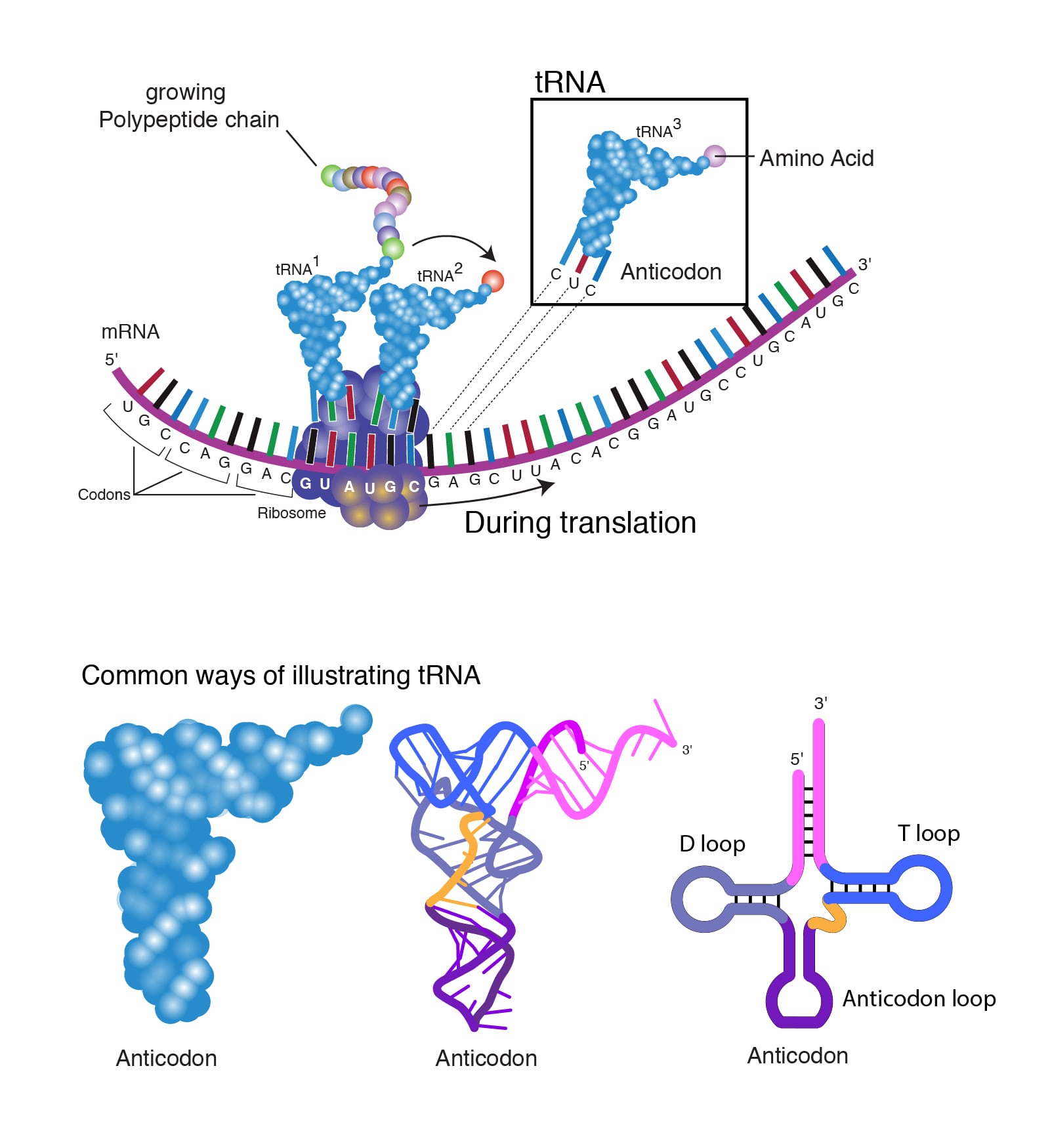
The large ribosomal subunit also contributes to the three tRNA binding sites:
The initiator methionine tRNA is the only aminoacyl-tRNA that can bind directly to the P site to start translation. At this point, the A site is aligned with the second mRNA codon. The ribosome is now ready to bind the second aminoacyl-tRNA at the A site, and the first peptide bond will form between this amino acid and the initiator methionine.
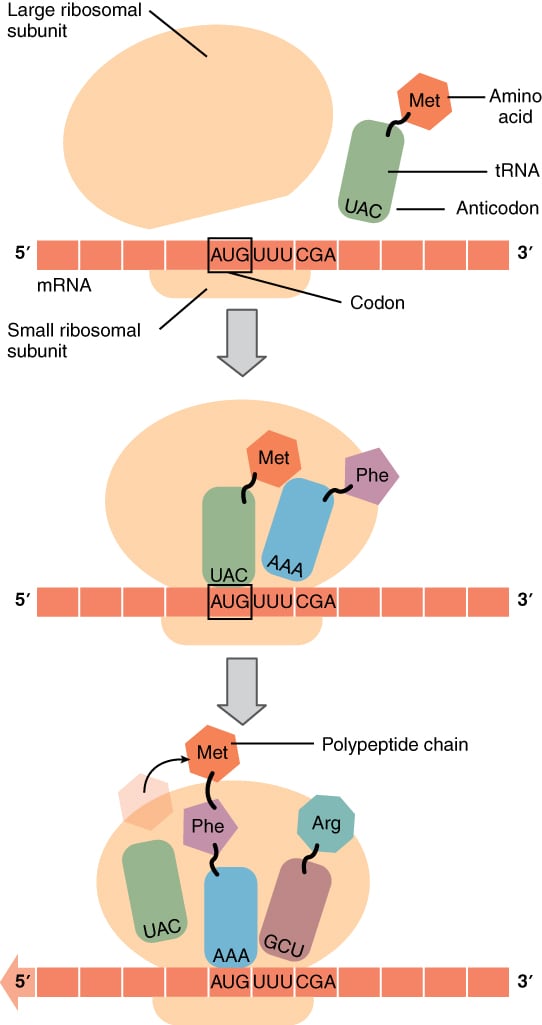
After the peptide bond forms, the ribosome translocates again. This shift moves the tRNA that no longer carries an amino acid into the E site, where it is released into the cytoplasm to pick up another amino acid. The A site becomes empty and ready to receive the next aminoacyl-tRNA. This cycle repeats until all codons in the mRNA have been read.
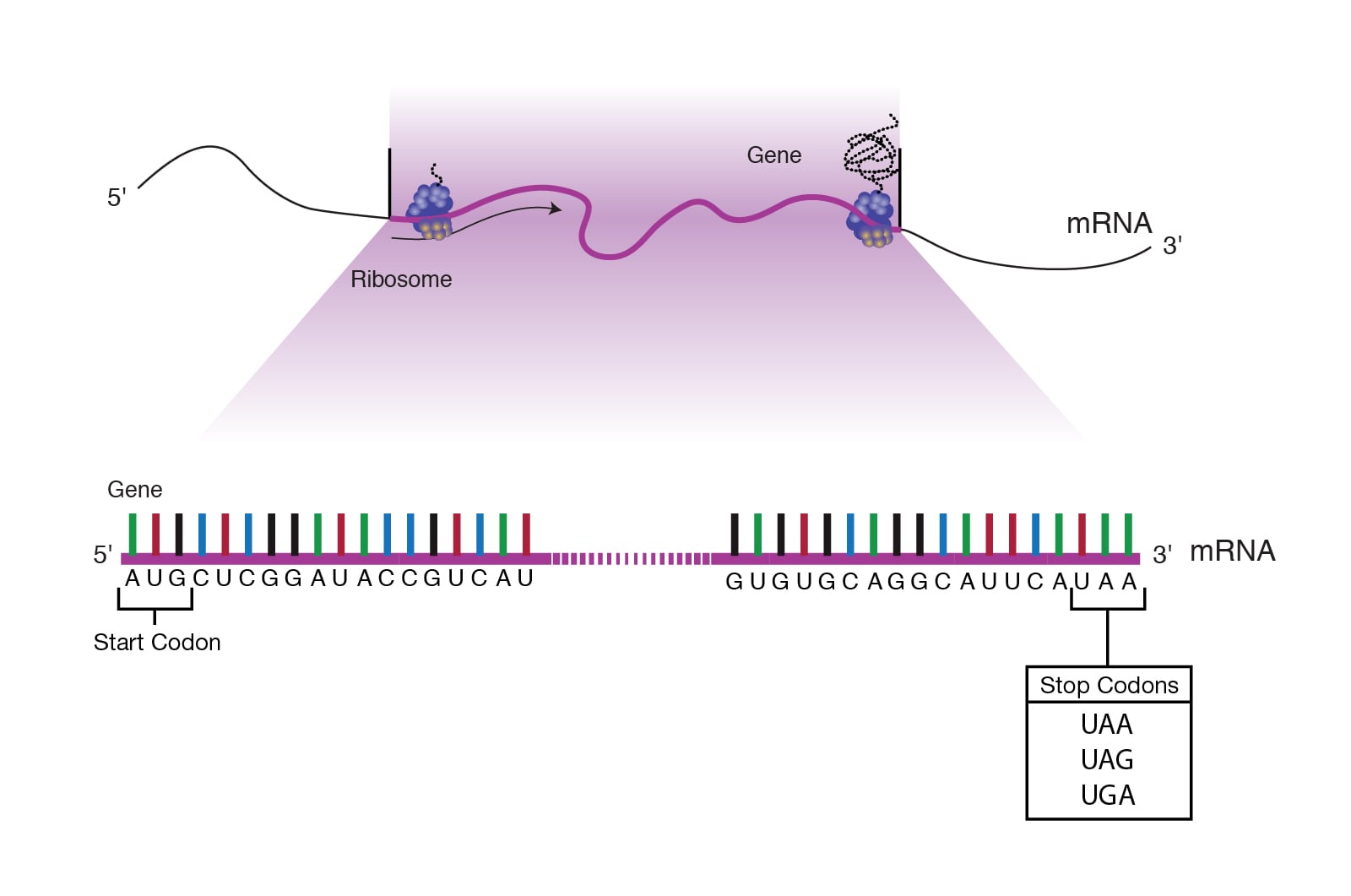
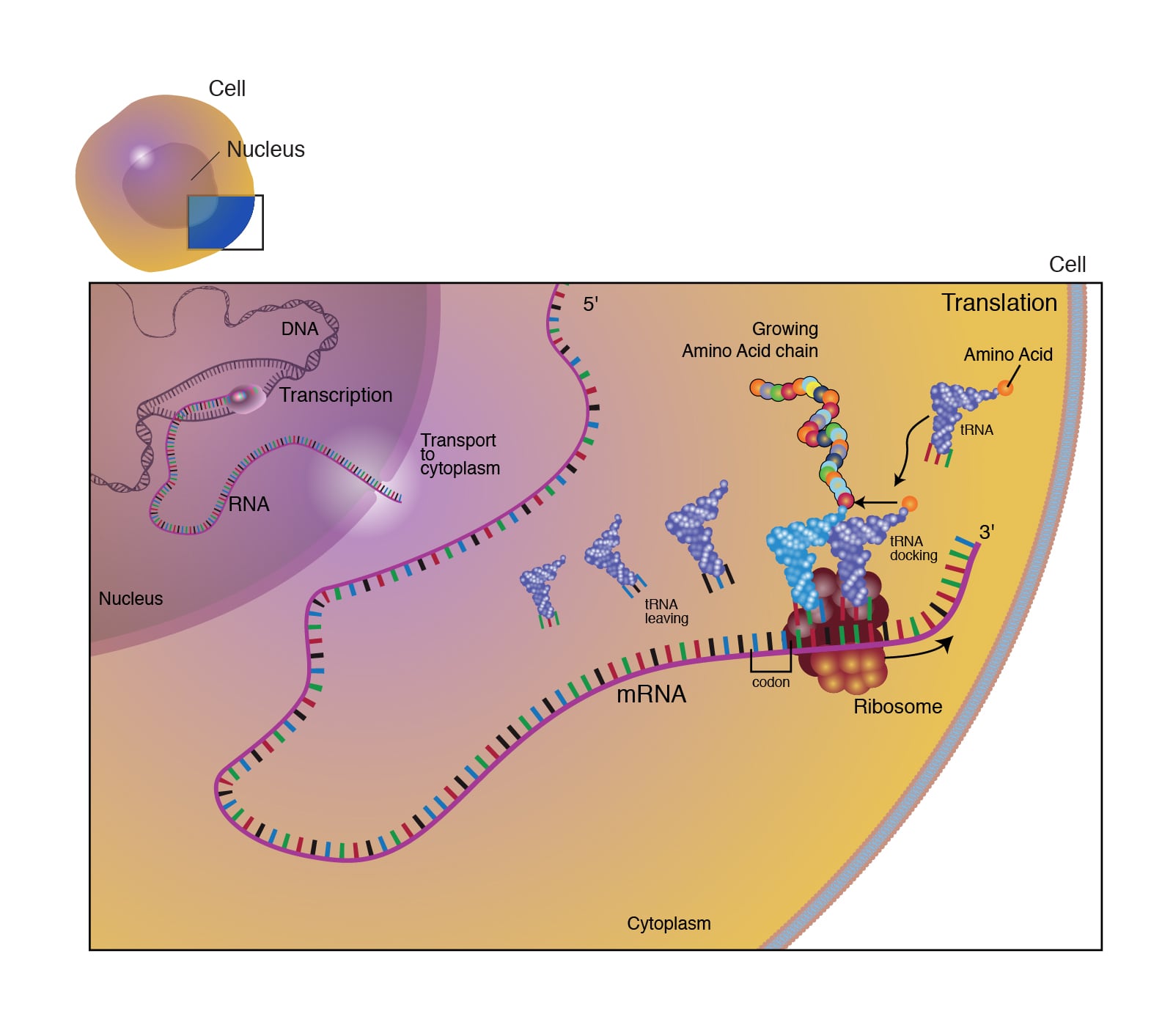
Post-translational modifications: Proteins and polypeptides are modified after translation to become fully functional. Following modifications are seen :