Nucleus and nucleolus
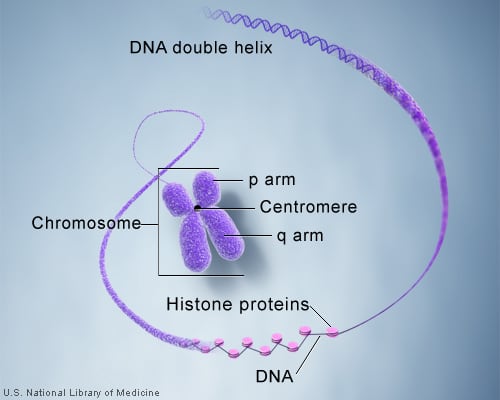
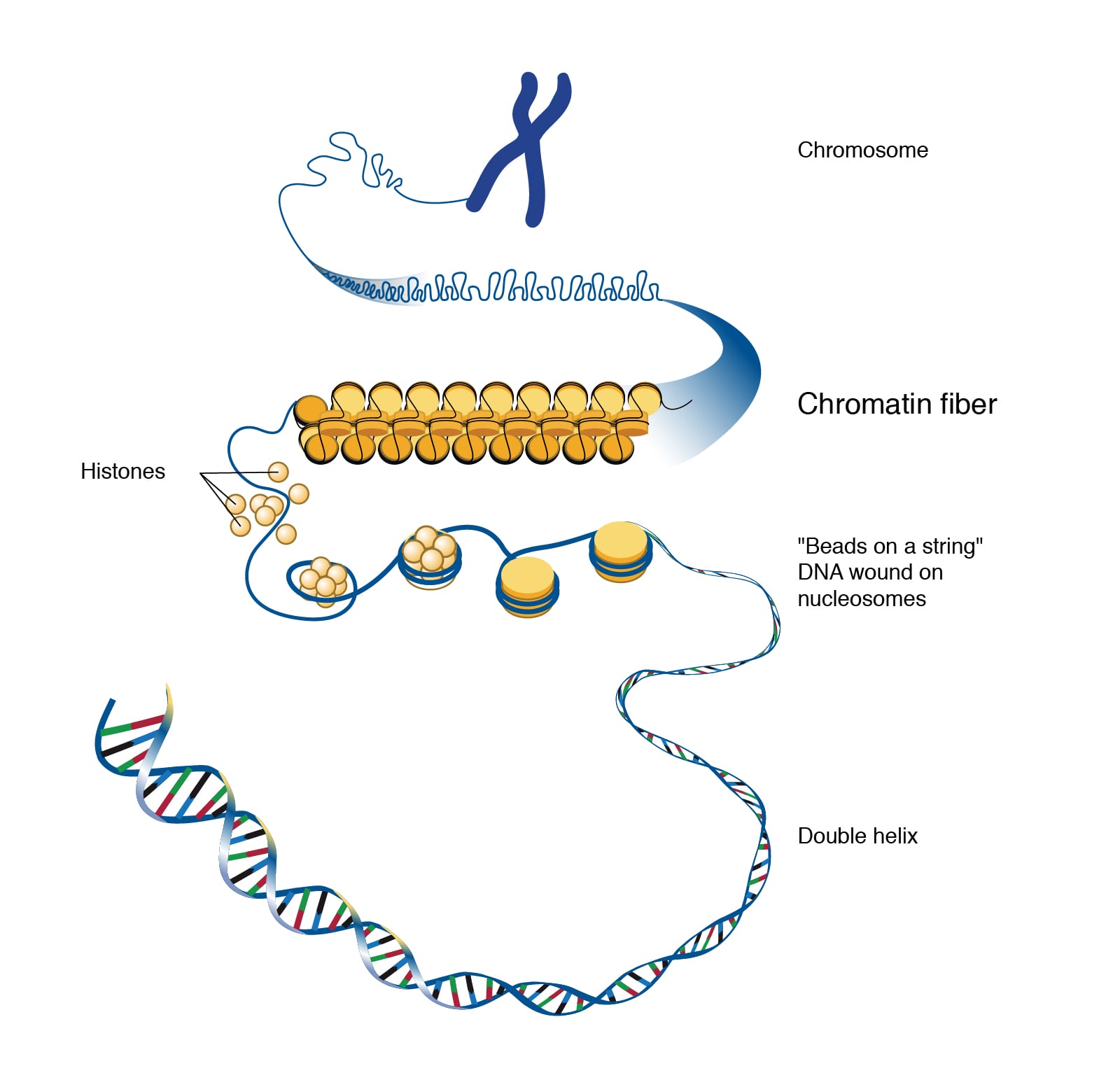
Nucleus and nucleolus: The nucleus is surrounded by a double nuclear membrane (nuclear envelope). The outer membrane is continuous with the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Nuclear pores are present in the nuclear membrane and allow transport between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Inside the nucleus, one or more darkly staining spherical bodies called nucleoli are present. The nucleolus is the site where ribosomes are assembled. DNA associated with histone proteins forms chromatin.
Comparison between euchromatin and heterochromatin
Euchromatin
- Contains transcriptionally active DNA
- More abundant
- Dispersed
- Acetylation of histone proteins essential for gene activation
Heterochromatin
- Transcriptionally inactive
- Less abundant
- Condensed
- Barr body is made of heterochromatin
- Methylation of DNA represses transcription
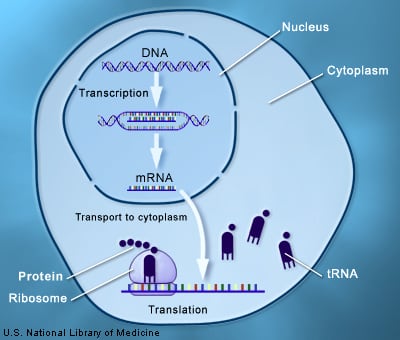
Transcription: Transcription is the process of transferring genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA (mRNA). It begins when RNA polymerase II binds to promoter regions of DNA. This binding forms an initiation complex made of RNA polymerase II and transcription factors.
TATA box: A promoter sequence located upstream of the start site. Transcription is initiated at the TATA box. It binds transcription factors such as TATA binding protein (TBP).
CAAT box: Located within the promoter region, upstream of the start site. It binds transcription factors like NF1.
GC box: Located upstream of the TATA box. It binds transcription factors like SP 1, WT, and zinc-finger proteins.
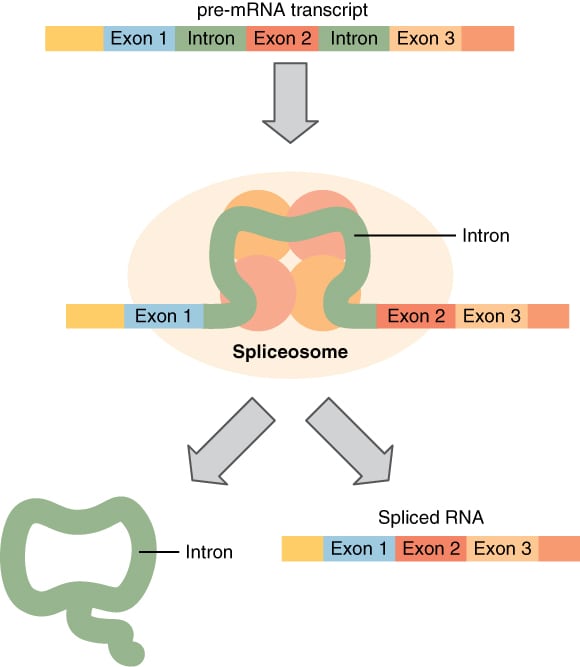
RNA polymerase II synthesizes the mRNA strand as a primary transcript called heterogenous nuclear RNA (hnRNA). hnRNA contains both exons (coding sequences) and introns (non-coding sequences).
Post-translational processing of primary RNA transcript
- Capping: Addition of 7-methylguanosine to the 5’ end of the RNA transcript. Capping protects RNA from degradation by exonucleases and helps with transport from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, splicing, and attachment to the 40S ribosome.
- Polyadenylation: Addition of about 200 adenosine moieties to the 3’ end of the RNA transcript. It protects RNA and helps with transport from the nucleus and recognition by ribosomes.
- Splicing: Removal of introns and joining of exons. Splicing is carried out by the spliceosome, which is composed of small nuclear RNAs (snRNA) associated with proteins to form small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (snRNPs). The junction of exons to introns is called a splice site. Antibodies to snRNPs are found in SLE.
Alternative splicing is a physiological process that allows a single gene to produce tissue-specific protein variants (isoforms) with different cellular functions or properties. It occurs by changing which intron and exon elements are joined during splicing, which alters the mRNA coding sequence. Alternate splicing accounts for 25000 human protein-coding genes being able to generate >90,000 different proteins. Aberrant splicing is seen in many diseases including cancers and beta thalassemia.
Regulation of gene expression: Following factors are important:
i) Only euchromatin is accessible to RNA polymerase II and transcription factors. Heterochromatin is not transcriptionally active.
ii) The rate of binding of RNA polymerase is determined by transcription factor binding to TATA, CAAT and GC boxes in the promoter region.
iii) Enhancers are DNA sequences located upstream or downstream from the promoter region. They bind to regulatory elements like transcription factors and increase the rate of transcription.
iv) Silencers are DNA sequences that bind regulatory elements called repressors leading to decrease in transcription. They can be located either near or away from the promoter, including within the intron.
v) Steroids, growth factors and hormones affect transcription directly and indirectly.