They’re virulent organisms associated with a wide range of human infections, from boils to sepsis.
Staphylococci are Gram-positive cocci arranged in grape-like clusters. They’re typically non-capsulated, except for a few strains that have a microcapsule (a thin polysaccharide layer).
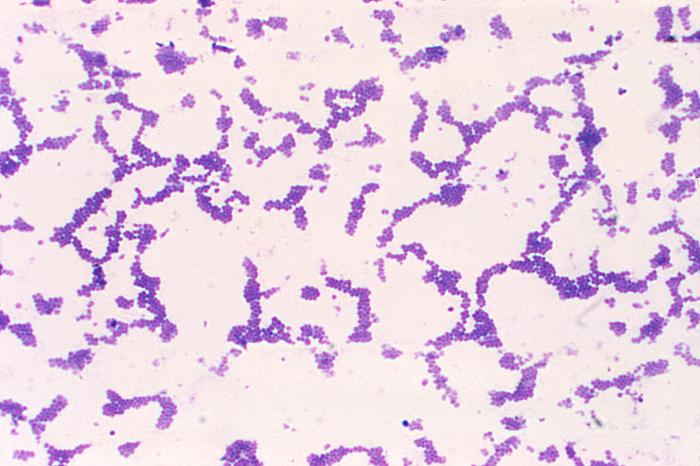
Numerous, spherical (cocci), Gram-positive, Staphylococcus aureus bacteria.
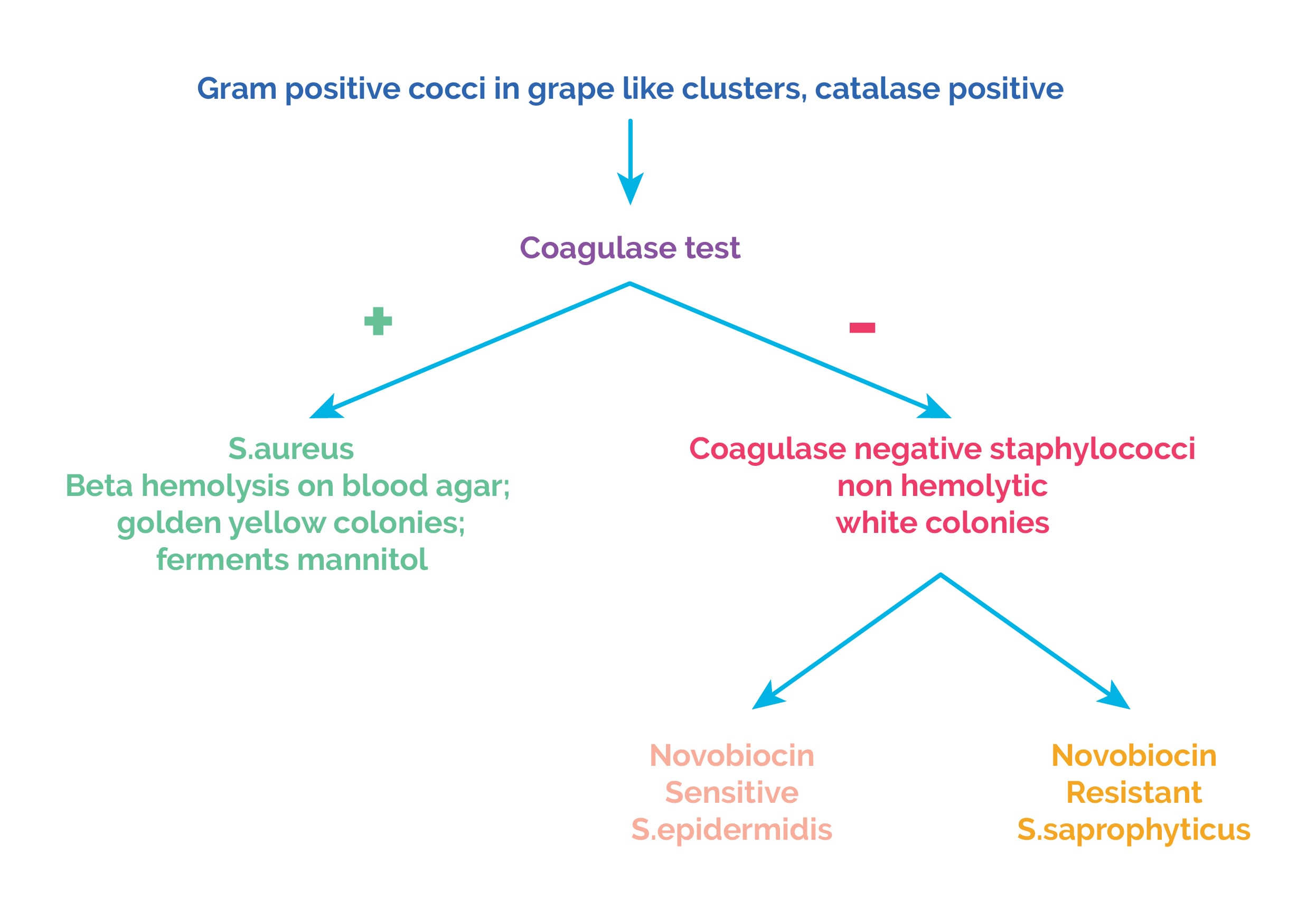
Staphylococci are classified based on the coagulase test:
All staphylococci are catalase positive.
Coagulase is an enzyme that converts soluble fibrinogen in plasma into insoluble fibrin.
Catalase breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. This helps bacteria survive inside human macrophages.
S. aureus causes many pyogenic infections, including boils, folliculitis, abscess, cellulitis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis, impetigo, and sepsis. It also causes toxin-mediated diseases, including food poisoning (enterotoxin), toxic shock syndrome (TSST toxin), and scalded skin syndrome (exfoliatin).
Symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea begin within 30 minutes to 8 hours after ingestion of contaminated food. Commonly implicated foods include sliced meats, pastries, sandwiches, and puddings.
This illness is due to preformed enterotoxin in contaminated food, so antibiotics don’t help.
This can present like septicemia, with fever, shock, hypotension, a desquamative reddish macular rash, and end-organ failure. It’s due to TSST toxin, which acts as a superantigen.
Patients often have a history of tampon use, recent childbirth, or staphylococcal infections such as infected burns or wounds.
This is mostly seen in young children. It’s characterized by fever, blisters, and skin peeling with a positive Nikolsky sign (skin peels off with gentle pressure). It’s caused by the toxin exfoliatin.
S. epidermidis causes device- or implant-associated infections, including intravenous catheter-associated sepsis, prosthetic heart valve endocarditis, intraperitoneal catheter-associated peritonitis, and prosthetic joint-associated arthritis. This is attributed to glycocalyx production by S. epidermidis.
S. saprophyticus causes urinary tract infections in young sexually active women.
Beta-lactamase-producing S. aureus can be treated with oxacillin, nafcillin, cephalosporins, amoxicillin plus clavulanic acid, and vancomycin.
MRSA is treated with vancomycin or daptomycin. For minor or skin MRSA infections, treat with trimethoprim plus sulfamethoxazole or clindamycin.
VRSA strains are treated with daptomycin or quinupristin dalfopristin.
S. epidermidis infections are treated with vancomycin.
S. saprophyticus infections are treated with quinolones or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.
Important points
Always do Gram stain and culture of pus from infected sites.
In toxic shock syndrome, blood cultures may be negative, but cultures from the source of infection will be positive.
Bacteriophage typing can be used for epidemiological purposes to trace the source of an outbreak.
Sign up for free to take 3 quiz questions on this topic